- Title
-
LCC-09, a Novel Salicylanilide Derivative, Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effect in Vascular Endothelial Cells
- Authors
- Angom, R.S., Zhu, J., Wu, A.T.H., Sumitra, M.R., Pham, V., Dutta, S., Wang, E., Madamsetty, V.S., Perez-Cordero, G.D., Huang, H.S., Mukhopadhyay, D., Wang, Y.
- Source
- Full text @ J Inflamm Res
|
LCC-09 reduces TNFα-induced leukocyte adhesion on endothelial cells. (A) Chemical structure of LCC-09. (B–D) HUVECs were pre-treated with LCC-09 or control DMSO vehicle control for 30 mins at the indicated concentrations and then stimulated with TNFα (5 ng/mL) for 6 h. qPCR was performed (N=4 per group) and expressed as relative folds of control group, which was normalized to 1. (E and F) HUVECs were co-cultured with LCC-09 (5 μM) or DMSO vehicle control for 30 mins and then stimulated with TNFα (5 ng/mL) for 20 h. Then HUVECs were co-cultured with CMFDA-labeled monocytic THP1 cells for 30 mins and adhered monocytes were imaged (D) and counted (E). *p<0.05; **p<0.01. |
|
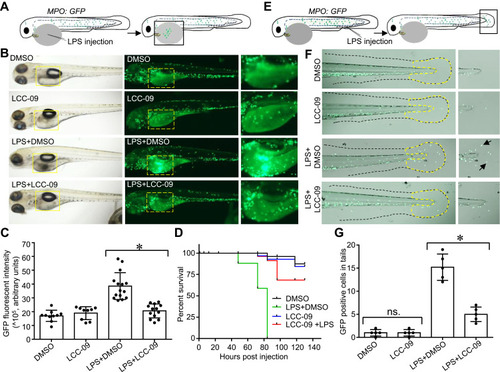
LCC-09 inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response in zebrafish. (A–D) Zebrafish (MPO;GFP) embryos at 48 hpf were treated with LCC-09 (5 μM) and DMSO as control for 3 h and then injected with LPS (0.4 mg/mL, 2 nL) through yolk sac. Images were collected 12 h after injection (B). Local accumulation of neutrophils was quantified using GFP fluorescent intensity and compared (C). Zebrafish survival was monitored (N=8 per group) (D). (E–G) LPS (0.4 mg/mL, 2 nL) was intravenously injected to the caudal vein of zebrafish (MPO;GFP) embryos at 48 hpf. Images were collected 6 h post-injection. Neutrophil accumulation in tail fins (outlined by yellow dotted dash lines) was counted and compared. Arrow denotes infiltration of GFP positive neutrophils induced by LPS injection. *p<0.05. |
|
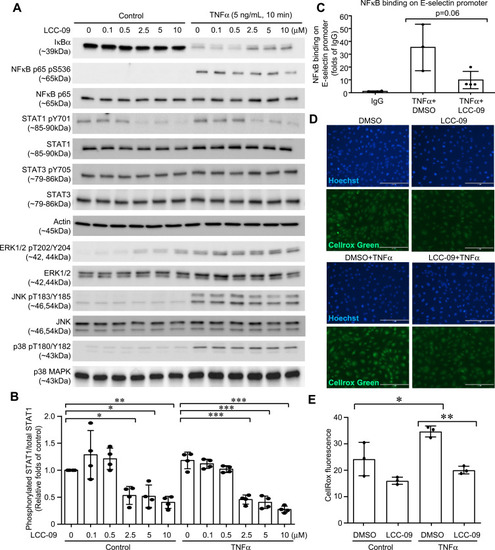
LCC-09 inhibits activation of NFκB and STAT1, and ROS generation in endothelial cells. HUVECs were pre-treated with LCC-09 and control DMSO for 30 mins at the indicated concentrations and then stimulated with TNFα (5 ng/mL). (A and B) Cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting. (C) ChIP was performed to examine the binding of NFκB to E-selectin promoter 2 h after TNFα stimulation. (D and E) Cells were stained with Cellrox Green and imaged (D). Fluorescent intensity was measured with a SpectraMax plate reader and compared (E) 30 mins after TNFα stimulation. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. |
|
Molecule docking model of LCC-09. LCC-09 (green color sticks) was docked in JAK1 (PDB ID 6W8I) (A), JAK2 (PDB ID 6AAJ) (B), JAK3 (PDB ID 1YVJ) (C), STAT1 (PDB ID 1BF5) (D), IKKβ (PDB ID 4KIK) (E) and NEMO (PDB ID 3BRT) (F). |
|
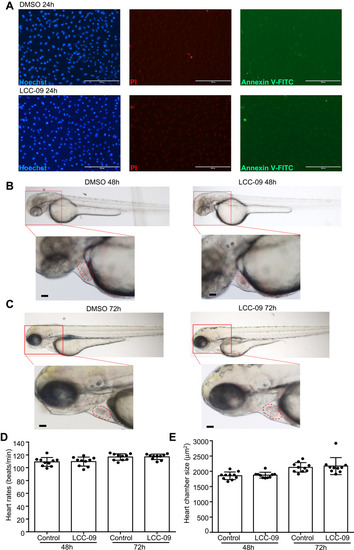
LCC-09 does not induce toxicity in cultured endothelial cells or zebrafish embryos. (A) HUVECs were cultured with LCC (10 μM) or DMSO control for 24 h and then stained with Hoechst, PI and annexin V-FITC. Images are representative of 3 independent experiments. (B–E) Zebrafish embryos at 6 hpf were incubated with LCC-09 (10 μM) or DMSO as control for 48 and 72 h, respectively. Heart rates and chamber sizes were measured and compared. Scale bar: 200 μM (A), 50 μM (B and C). |