- Title
-
lncRNA HOTAIR overexpression induced downregulation of c-Met signaling promotes hybrid epithelial/mesenchymal phenotype in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- Authors
- Topel, H., Bagirsakci, E., Comez, D., Bagci, G., Cakan-Akdogan, G., Atabey, N.
- Source
- Full text @ Cell Commun. Signal.
|
Expression of HOTAIR and c-Met in HCC cell lines and patient tissues through HCC progression. RT-qPCR analysis of ( |
|
Effect of HOTAIR overexpression in c-Met downstream signaling. Analysis of c-Met and downstream signaling in MOCK and HOTAIR OE cells. Immunoblot analysis of ( |
|
Analysis of HOTAIR-c-Met interaction in MET overexpressed, activated and inhibited conditions. Immunoblotting of (a) c-Met activation phosphorylation (Tyr-1234/Tyr-1235), and total c-Met protein expression. Confocal microscopy imaging of (b) c-Met protein and RT-qPCR analysis of c-Met mRNA expression in MET OE SNU-398 clones. (c) Confocal imaging of FISH labeling (white dots) and RT-qPCR analysis of HOTAIR mRNA expression in MET OE clones. (d) Confocal imaging of Caveolin-1 protein and qPCR analysis of CAV1 mRNA expression in MET OE cells. (e) Immunoblot of c-Met activation and qPCR analysis of HOTAIR expression in ligand-dependent activation (HGF 10 ng/ml) of c-Met in HuH-7, HEP-3B, SNU-449, MAHLAVU and SK-HEP-1 cells. RT-qPCR analysis of HOTAIR expression (f), in response to heparin (100 μg/mL) induced c-Met activation in SK-HEP-1 cells. RT-qPCR analysis of MET and HOTAIR expressions in sorafenib resistance (MAHLAVU cell line) (g) and high-glucose (25 mM, HuH-7 cell line) (h) and fluidic shear stress (0.5 dyn/cm2, HuH-7 cell line) (i) induced c-Met activations. (j) Immunoblot of c-Met activation and qPCR analysis of HOTAIR expression in tyrosine kinase activity inhibition of c-Met by SU11274 (2500 nM) HuH-7, SNU-449, MAHLAVU and SK-HEP-1 cells. All graphs of experiments are presented as the mean ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, **** p ≤ 0.0001 |
|
HOTAIR OE induced c-Met inhibition decreases adhesion, proliferation and colony formation. Normalized cell index and slope analysis of adhesion to ( |
|
HOTAIR OE induced c-Met inhibition decreases individual motility and invasion ability of SNU-449 cells. Real-time (by xCELLigence RTCA) and end-point (cell culture inserts) analysis of motility and invasion of MOCK and HOTAIR OE cell clones. Normalized cell index of ( |
|
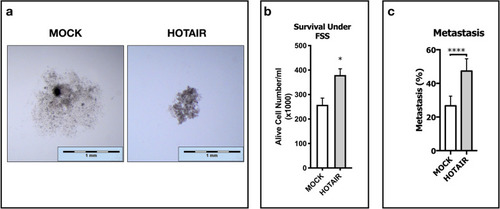
lncRNA HOTAIR suppresses c-Met induced cell scattering, enhances survival under FSS and promotes metastasis in zebrafish embryos. Spheroid formation, survival under fluidic shear stress and metastatic capacity of MOCK and HOTAIR OE cells. ( |
|
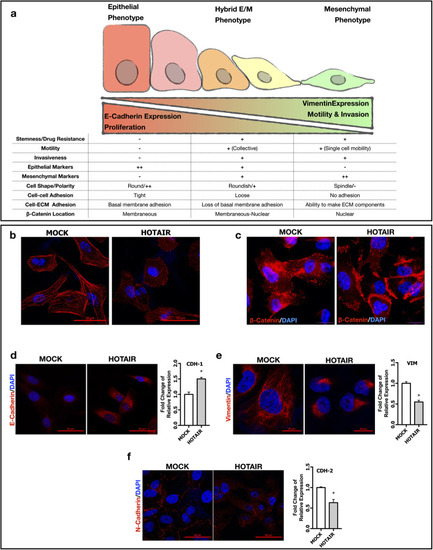
lncRNA HOTAIR maintains hybrid E/M phenotype to promote metastasis. ( |
|
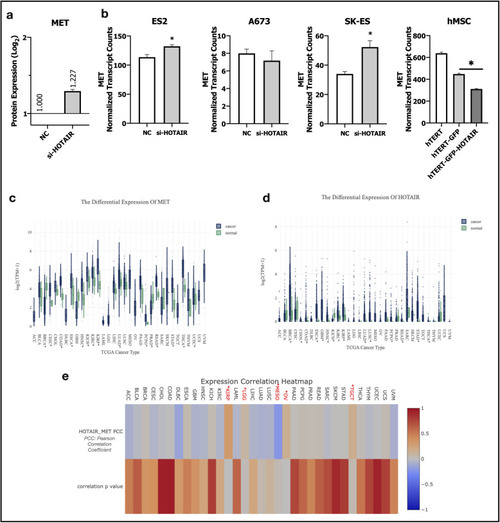
Bioinformatic analyses of GEO and TCGA datasets supports HOTAIR and c-Met interplay. ( |