- Title
-
Phloroglucinol and dieckol isolated from Ecklonia cava suppress impaired diabetic angiogenesis; A study of in-vitro and in-vivo
- Authors
- Hwang, J., Yang, H.W., Lu, Y.A., Je, J.G., Lee, H.G., Fernando, K.H.N., Jeon, Y.J., Ryu, B.
- Source
- Full text @ Biomed. Pharmacother.
|
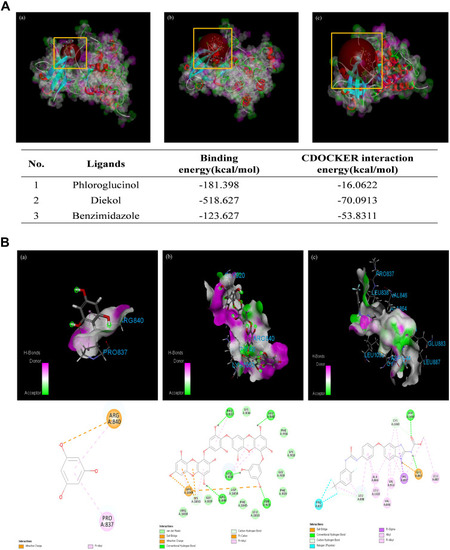
Molecular docking of phloroglucinol (PG) and dieckol (DK) with VEGFR-2. (A) Specific interactions between the ligands, (a) PG, (b) DK, and (c) benzimidazole and VEGFR-2 (PDB ID: 2OH4) following automated docking of the structures at the active site of VEGFR-2. Docking results of VEGFR-2 with PG, DK, and benzimidazole. (B) Favorable hydrogen-bond interactions in the ligand-VEGFR-2 complexes are displayed; pink represents the donors and green represents the acceptors. Two-dimensional (2D) diagram of the ligand-VEGFR-2 complexes (PG, DK, and benzimidazole). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.) |
|
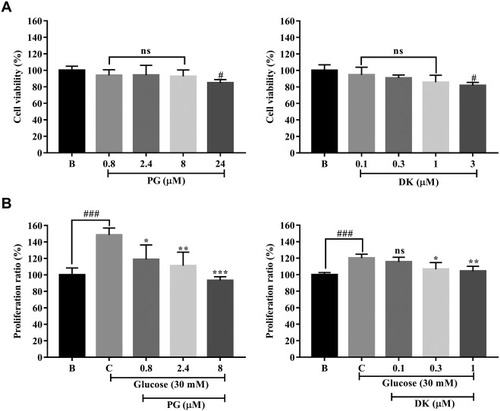
Effects of phloroglucinol (PG) and dieckol (DK) on the proliferation of EA.hy926 cells treated with a high concentration of glucose. (A) Cytotoxicity results of PG and DK in EA.hy926 cells using the MTT assay. (B) Antiproliferative effects of different concentrations of PG and DK in EA.hy926 cells under high glucose conditions. Cytotoxic and antiproliferative effects are expressed as percent values, with values for the blank group considered as 100%. The results were compared to those obtained for the control group (the second bar); data are expressed as mean ± SD of three independent experiments; ns, not significant, # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001 compared to the blank group (no sample treated group); * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 compared to the control group (30 mM glucose-treated group). |
|
Effects of phloroglucinol (PG) and dieckol (DK) on the migration of EA.hy 926 cells treated with a high concentration of glucose. (A) Images were acquired at the initial gap length (0 h) and final gap length (4 h) following treatment with PG in the cell-migration assay. (a) 0 mM glucose + 0 µM PG; (b) 30 mM glucose + 0 µM PG; (c) 30 mM glucose + 0.8 µM PG; (d) 30 mM glucose + 2.4 µM PG; and (e) 30 mM glucose + 8 µM PG; Quantitative evaluation of the inhibition of migration of EA.hy926 cells treated with a high glucose concentration after treatment with PG. (B) (a) 0 mM glucose + 0 µM DK; (b) 30 mM glucose + 0 µM DK; (c) 30 mM glucose + 0.1 µM DK; (d) 30 mM glucose + 0.3 µM DK; and (e) 30 mM glucose + 1 µM DK; Quantitative evaluation of the inhibition of migration of EA.hy926 cells treated with high glucose concentration after treatment with DK. The effect of 30 mM of glucose was compared to that of B; blank (0 mM glucose + 0 μM PG), ### p < 0.001. Percentage gap closure was normalized to that of C: control (30 mM glucose + 0 μM PG); ns, not significant, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. |
|
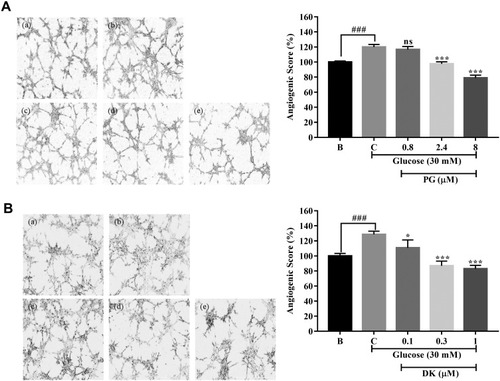
Effect of phloroglucinol (PG) and dieckol (DK) on the formation of tube-like structures in EA.hy926 cells cultured on Matrigel and treated with a high concentration of glucose. (A) Cells were incubated in a medium containing 1% penicillin/streptomycin for 12 h. Thereafter, the cells were replated on Matrigel-coated plates at a density of 5 × 103 cells/well. After 8 h, images of the cultures were captured using phase-contrast microscopy (4 × magnification). (a) 0 mM glucose + 0 µM PG; (b) 30 mM glucose + 0 µM PG; (c) 30 mM glucose + 0.8 µM PG; (d) 30 mM glucose + 2.4 µM PG; and (e) 30 mM glucose + 8 µM PG; Angiogenic score of the effect of PG on EA.hy926 cells treated with a high concentration of glucose. (B) (a) 0 mM glucose + 0 µM DK; (b) 30 mM glucose + 0 µM DK; (c) 30 mM glucose + 0.1 µM DK; (d) 30 mM glucose + 0.3 µM DK; and (e) 30 mM glucose + 1 µM DK; Angiogenic score of the effect of DK on EA.hy926 cells treated with a high concentration of glucose. The effect of 30 mM of glucose was compared to that of B; blank (0 mM glucose + 0 μM PG, DK), ### p < 0.001. Percentage gap closure was normalized to that of C: control (30 mM glucose + 0 μM PG, DK); ns, not significant, * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001. |
|
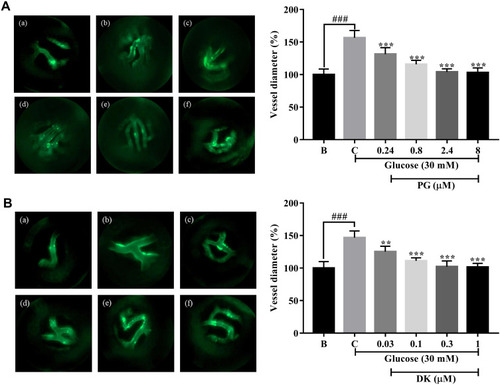
Inhibitory effects of phloroglucinol (PG) and dieckol (DK) on the increase in retinal vessel diameter in transgenic (flk:EGFP) zebrafish embryos treated with a high concentration of glucose. (A) Fluorescence images of the hyaloid retinal vessels of the transgenic zebrafish (flk:EGFP) embryos treated with PG. (a) 0 mM glucose + 0 µM PG; (b) 130 mM glucose + 0 µM PG; (c) 130 mM glucose + 0.24 µM PG; (d) 130 mM glucose + 0.8 µM PG; (e) 130 mM glucose + 2.4 µM PG; and (f) 130 mM glucose + 8 µM PG; Quantitation of the hyaloid retinal vessel diameter following treatment with PG. (B) Fluorescence images of the hyaloid retinal vessels of transgenic zebrafish (flk:EGFP) embryos treated with DK. (a) 0 mM glucose + 0 µM DK; (b) 130 mM glucose + 0 µM DK; (c) 130 mM glucose + 0.03 µM DK; (d) 130 mM glucose + 0.1 µM DK; (e) 130 mM glucose + 0.3 µM DK; and (f) 130 mM glucose + 1 µM DK; Quantitation of the hyaloid retinal vessel diameter following treatment with DK. The effect of 130 mM of glucose was compared to that of B; blank (0 mM glucose + 0 μM PG, DK), ### p < 0.001. Percentage gap closure was normalized to that of C: control (30 mM glucose + 0 μM PG, DK); ns, not significant, **p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. PHENOTYPE:
|