- Title
-
Microfibril-associated glycoprotein 4 (Mfap4) regulates haematopoiesis in zebrafish
- Authors
- Ong, S.L.M., de Vos, I.J.H.M., Meroshini, M., Poobalan, Y., Dunn, N.R.
- Source
- Full text @ Sci. Rep.
|
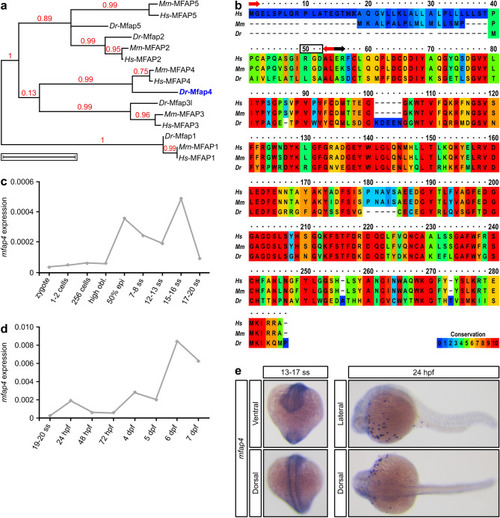
Alignment of vertebrate Mfap4 proteins and EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
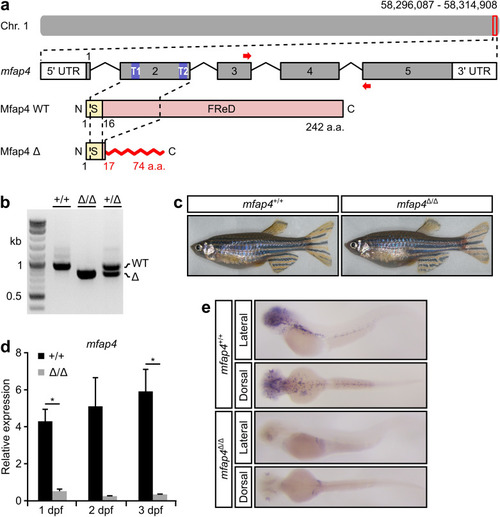
Generation of a loss-of-function mutation in zebrafish EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
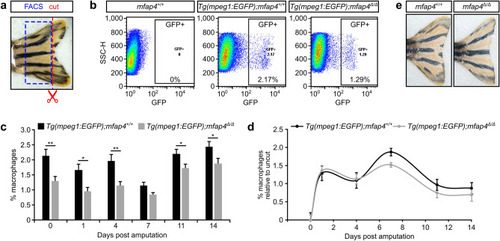
EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
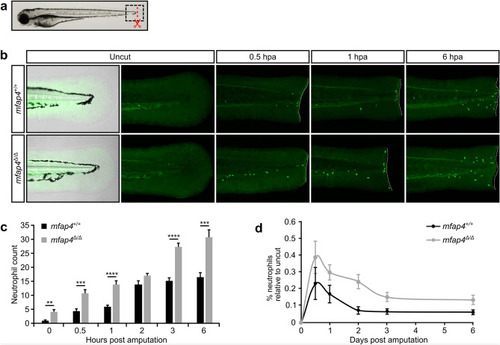
Neutrophil recruitment to the amputation site is increased in EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
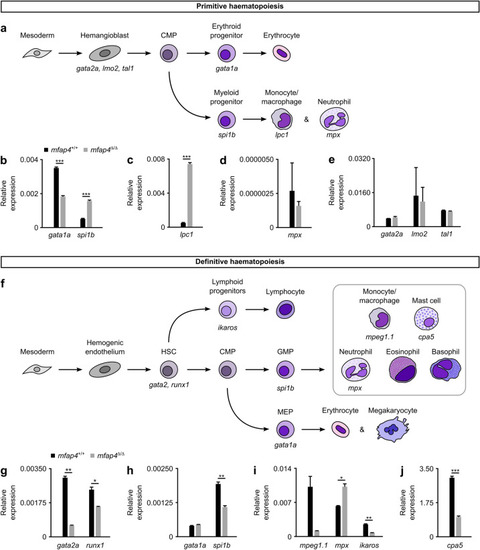
Loss of Mfap4 alters myeloid haematopoiesis in zebrafish. ( EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|