- Title
-
Eyes shut homolog (EYS) interacts with matriglycan of O-mannosyl glycans whose deficiency results in EYS mislocalization and degeneration of photoreceptors
- Authors
- Liu, Y., Yu, M., Shang, X., Nguyen, M.H.H., Balakrishnan, S., Sager, R., Hu, H.
- Source
- Full text @ Sci. Rep.
|
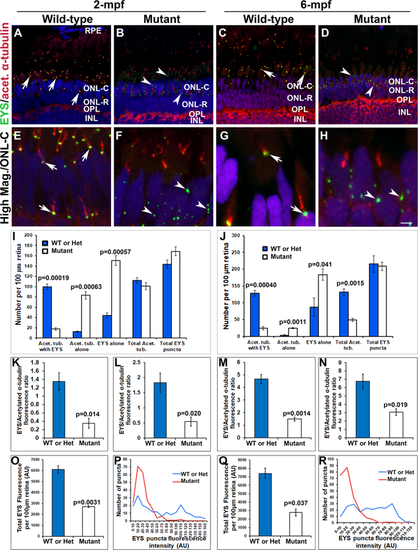
Mislocalization of EYS protein in pomgnt1 mutant zebrafish retina. Retinal sections from wild-type and pomgnt1sny7 mutant zebrafish were double immunostained with EYS (green fluorescence) and acetylated α-tubulin (red fluorescence). (A and E) Wild-type retina at 2-mpf. (C and G) Wild-type retina at 6-mpf. Most EYS-positive puncta in the wild-type retina were associated with basal end of the acetylated α-tubulin reactivity at both 2- and 6-mpf (arrows). (B and F) Homozygous pomgnt1sny7 mutant retina at 2-mpf. (D and H) Homozygous pomgnt1sny7 mutant retina at 6-mpf. Most EYS-positive puncta were not associated with acetylated α-tubulin but were localized in the outer nuclear layer at both 2- and 6-mpf (arrowheads). (I and J) Counting of EYS-acetylated α-tubulin double staining from the outer nuclear layer to the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) for 2-mpf and 6-mpf retina, respectively. Note that acetylated α-tubulin reactivity associated with EYS puncta was decreased in the mutant, and acetylated α-tubulin not associated with EYS puncta was increased in the mutant. EYS puncta not associated with acetylated α-tubulin was increased in the mutant. ANOVA; post-hoc Student’s t-test with Bonferroni correction.(K and L) Ratio of EYS and acetylated α-tubulin immunoreactivity for each acetylated α-tubulin-labeled axoneme in rods and cones at 2-mpf, respectively. Note that EYS immunoreactivity at the connecting cilium was reduced by about 5-fold in pomgnt1 mutant retina. Student’s t-test. (M and N) Ratio of EYS and acetylated α-tubulin immunoreactivity per acetylated α-tubulin-labeled axoneme in rods and cones at 6-mpf, respectively. Note that EYS immunoreactivity at the connecting cilium was also reduced in the pomgnt1mutant retina at 6-mpf. Student’s t-test. (O and Q) Total EYS immunoreactivity at 2-mpf and 6-mpf, respectively. Total EYS immunoreactivity was reduced in pomgnt1 mutant retina at both ages. Student’s t-test. (P and R) Histogram representation of total EYS immunoreactivity between wild-type/heterozygous and mutant fish at 2-mpf and 6-mpf, respectively. Note the shift in the number of EYS puncta to lower fluorescence intensities in the pomgnt1 mutant fish at both ages. Scale bar in H: 5 µm for A-D; 2.5 µm for E-H. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
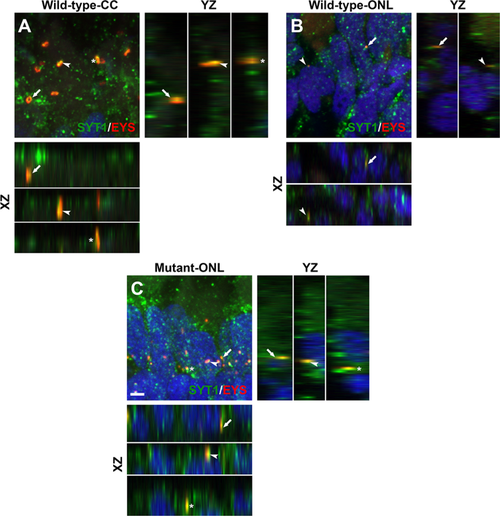
Mislocalized EYS in pomgnt1 mutant zebrafish retina was co-localized with synaptogamin-1. Retinal sections from 2-mpf zebrafish were double stained with antibodies against EYS (red fluorescence) and synaptotagmin-1 (green fluorescence). (A) Wild-type inner/outer segment layers showing connecting cilia (CC). Maximal projection and its orthogonal views of three double stained puncta are shown. EYS-immunoreactivity was co-localized with synaptagmin-1 reactivity. (B) Wild-type outer nuclear layer (ONL). Maximal projection and its orthogonal views of two double stained puncta are shown. EYS-immunoreactivity was co-localized with synaptagmin-1 reactivity. (C) Homozygous pomgnt1sny7 mutant outer nuclear layer. Maximal projection and its orthogonal views of three double stained puncta are shown. Mislocalized EYS immunoreactive puncta was co-localized with synaptotagmin-1 reactivity. Scale bar in C: 2 µm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Loss of photoreceptors in pomgnt1 mutant retinas at 6-mpf but not 2-mpf. Retinal sections from 2-mpf and 6-mpf zebrafish were immunostained with GNAT2 antibody (green fluorescence, A–D) and 1D4 (green fluorescence, E–H). The sections were counter-stained with DAPI. To quantify photoreceptors, DAPI fluorescence confocal images of dorsal and ventral retinas from the optic nerve head to the ciliary margin were each divided into 5-equal compartments. Nuclei within the outer nuclear layer of each compartment were counted (M and N). GNAT2 and 1D4 immunoreactive intensities were measured (I–L). (A) Wild-type GNAT2 immunostaining at 2-mpf. (B) Homozygous pomgnt1sny7 mutant GNAT2 immunostaining at 2-mpf showing similar immunoreactivity compared to wild-type. (C) Wild-type GNAT2 immunostaining at 6-mpf. (D) Homozygous pomgnt1sny7 mutant GNAT2 immunostaining at 6-mpf showing reduced immunoreactivity compared to wild-type. (E) Wild-type 1D4 immunostaining at 2-mpf. (F) Homozygous pomgnt1sny7 mutant 1D4 immunostaining at 2-mpf showing similar immunoreactivity compared to the wild-type. (G) Wild-type 1D4 immunostaining at 6-mpf. (H) Homozygous pomgnt1sny7 mutant 1D4 immunostaining at 6-mpf showing reduced immunoreactivity compared to the wild-type. (I) GNAT2 immunofluorescence intensity quantification of wild-type and mutant fish at 2-mpf. There was no significant difference between wild-type and mutant retinas. (J) 1D4 immunofluorescence intensity quantification of wild-type and mutant fish at 2-mpf. There was no significant difference between wild-type and mutant retinas. (K and L) GNAT2 and 1D4 immunofluorescence intensity (artificial units, AU) in the mutant retina was reduced at 6-mpf. Student’s t-test. (M) Nuclei counting of outer nuclear layer at 2-mpf. There was no significant difference between wild-type and mutant retinas. (N) Nuclei counting of outer nuclear layer at 6-mpf. Nuclei within the outer nuclear layer in the mutant were reduced in number compared to wild-type. P = 0.00026; repeated measures ANOVA. (Oand P) 2-mpf nuclei count in the ONL-R and ONL-C retinal layers, respectively. There was no significant difference between wild-type and homozygous pomgnt1sny7 mutants. (Q and R) 6-mpf nuclei count in the ONL-R and ONL-C retinal layers, respectively. Note the significant reduction of nuclei in both ONL-R and ONL-C in homozygous pomgnt1sny7 mutants at 6-mpf. Together, these results indicated photoreceptor degeneration in mutant retina. Student’s t-test. Scale bar in H: 5 µm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
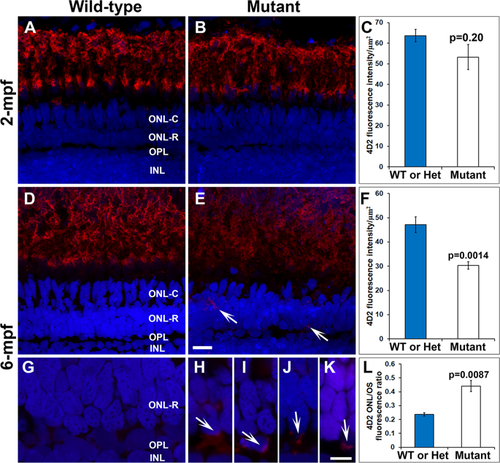
Reduction and mislocalization of rhodopsin in pomgnt1 mutant retina. Retinal sections from 2-mpf and 6-mpf zebrafish were immunostained with antibody 4D2 (red) and counter-stained with DAPI (blue). (A) 4D2 immunostaining of wild-type retina at 2-mpf. (B) 4D2 immunostaining of homozygous pomgnt1sny7 mutant retina at 2-mpf. (C) Quantification of 4D2 fluorescence intensity at 2-mpf. There was no significant reduction in 4D2 intensity in the mutant fish at this age. Student’s t-test. (D) 4D2 immunostaining of wild-type retina at 6-mpf. (E) 4D2 immunostaining of homozygous pomgnt1sny7 mutant retina at 6-mpf. Note the reduction in 4D2 fluorescence intensity. Note the mislocalization of 4D2 immunoreactivity to the ONL-R (arrows). (F) Quantification of 4D2 fluorescence intensity at 6-mpf. There was a significant reduction in 4D2 intensity in the mutant fish at this age. Student’s t-test. (G) High mag of wild-type 4D2 staining at 6-mpf. Fluorescence intensity of 4D2 in the ONL-R was low. (H–K) High mag of homozygous pomgnt1sny7 mutant 4D2 staining at 6-mpf. Note the mislocalization of 4D2 immunoreactivity to the ONL-R layer (arrows). (L) Ratio of 4D2 fluorescence intensity of outer nuclear layer/outer segment layer (ONL/OS). 4D2 ONL/OS fluorescence ratio was increased in the mutants. Student’s t-test. Scale bar in E: 5 µm for A, B, D and E; scale bar in K: 5 µm for G-K. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
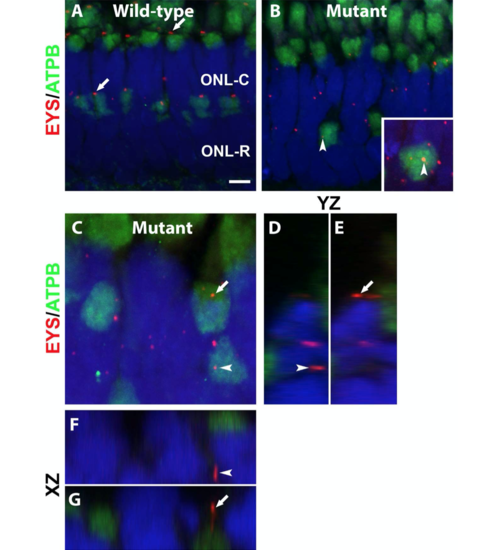
Mislocalized EYS in pomgnt1 mutant photoreceptors was not localized with mitochondria.
(C-G) Mutant. Max projection image and its orthogonal views of EYS puncta that appeared to be over the ATPB immunoreactive domains. Of 81 EYS immunoreactive puncta that appeared to overlap with ATPB immunoreactivity, none were within the ATPB immunoreactive domain, indicating that mislocalized EYS were not within mitochondria. Scale bar in A: = 4.36 m for A-B, 2 m for C. |
|
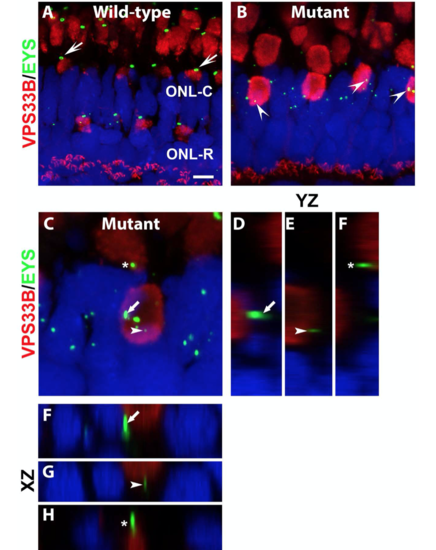
Mislocalized EYS in pomgnt1 mutant photoreceptors was not localized with late endosomes/lysosomes.
(C-H) Mutant. Max projection image and its orthogonal views of EYS puncta that appeared to be over the ATPB immunoreactive domains. Of 62 EYS immunoreactive puncta that appeared overlapping with VPS33B immunoreactivity, none were within the VPS33B immunoreactive domain, indicating that mislocalized EYS puncta were not located in late endosomes/lysosomes. |
|
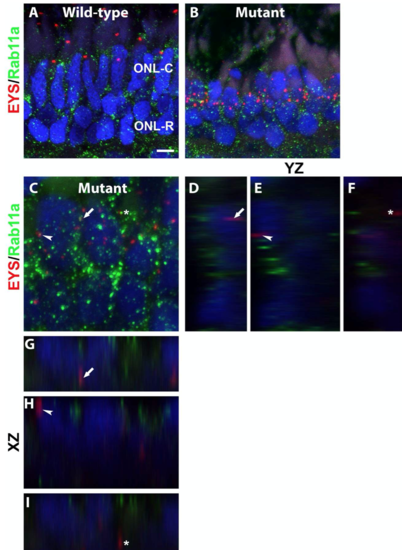
Mislocalized EYS in pomgnt1 mutant photoreceptors was not localized with the recycling endosomes.
(C-I) Mutant. Max projection and its orthogonal views of EYS puncta that appeared to overlap with the Rab11a immunoreactive puncta. Of 20 EYS puncta that appeared to overlap with Rab11a immunoreactive puncta, none were co-localized with Rab11a reactivity. Scale bar in A: 4.36 m for A-B, 2 m for C. |