- Title
-
Exosomal Thrombospondin-1 Disrupts the Integrity of Endothelial Intercellular Junctions to Facilitate Breast Cancer Cell Metastasis
- Authors
- Cen, J., Feng, L., Ke, H., Bao, L., Li, L.Z., Tanaka, Y., Weng, J., Su, L.
- Source
- Full text @ Cancers
|
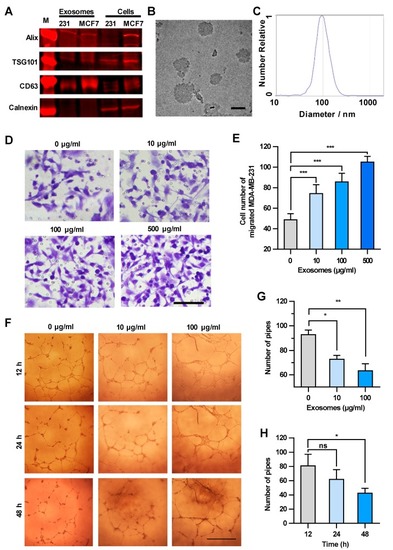
The cancer cell-derived culture supernatant and the exosome-enriched fraction significantly enhance the transendothelial migration of breast cancer cells. ( |
|
Exosomes enhance the transendothelial migration of breast cancer cells and inhibit the HUVEC tube formation. ( |
|
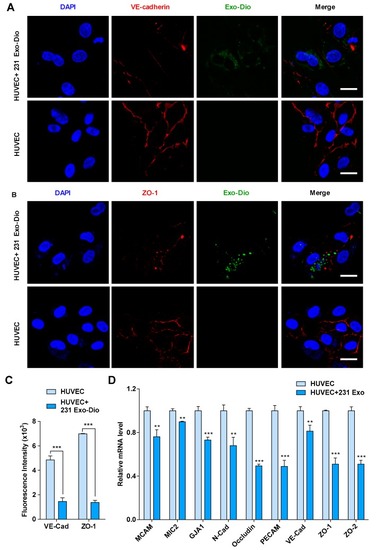
Exosomes derived from MDA-MB-231 cells regulate the expression of intercellular junction molecules in HUVECs. ( |
|
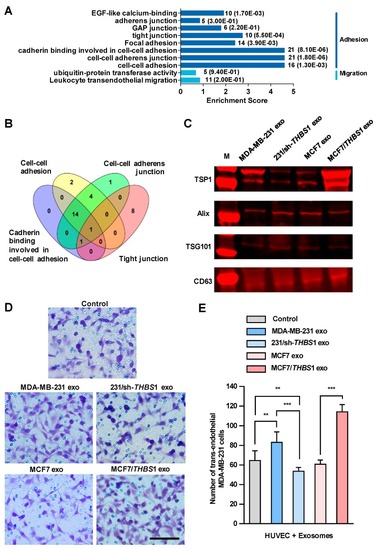
Exosomal thrombospondin-1 (TSP1) enhances the transendothelial migration of breast cancer cells. ( |
|
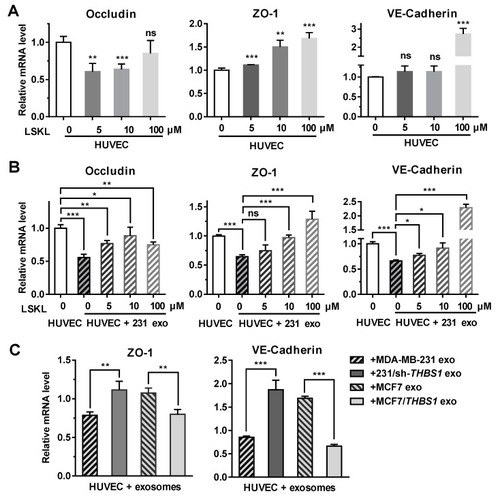
Exosomal TSP1 derived from breast cancer cells suppresses the expression of HUVEC intracellular junction proteins. ( |
|
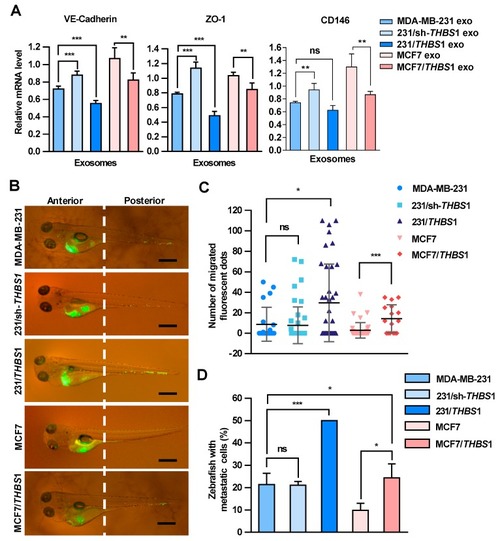
Carcinoma-derived exosomal TSP1 promotes the transendothelial migration of tumor cells in zebrafish. ( PHENOTYPE:
|
|
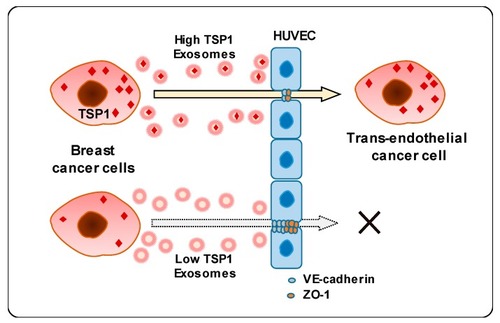
Schematic diagram of transendothelial migration of breast cancer cells with high TSP1 expression via cancer cell-derived exosomes. |