- Title
-
Effect of JNK inhibitor SP600125 on hair cell regeneration in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae
- Authors
- He, Y., Cai, C., Sun, S., Wang, X., Li, W., Li, H.
- Source
- Full text @ Oncotarget
|
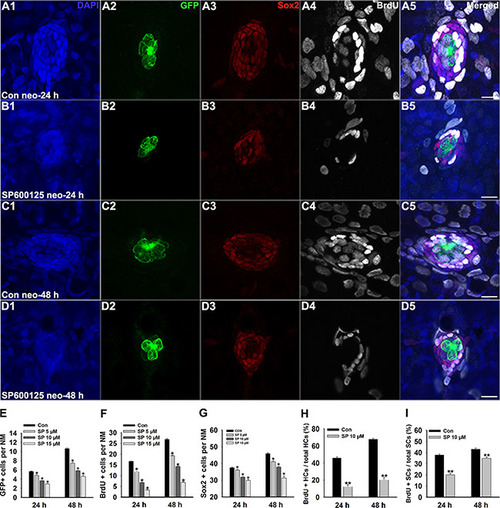
SP600125 decreases regeneration of hair cells in zebrafish lateral line neuromasts. (A–D) We treated 5 dpf Tg(Brn3c:mGFP) zebrafish with 400 μM neomycin for 1 h and then treated them for 24 h or 48 h with 10 μM SP600125 and subsequently imaged GFP-positive hair cells (green), Sox2-positive supporting cells (red), and BrdU-positive replicating cells (white). SP600125 significantly decreased the numbers of GFP-positive hair cells and Sox2-positive supporting cells in neuromasts as well as reduced the proportion of cells in S-phase as indicated by BrdU staining. Scale bars = 10 μm. Higher magnification of hair cells and supporting cells of the neuromast taken from z-stacks show that hair cells and supporting cells in untreated controls and SP600125-treated animals had no observable morphological differences though there were fewer GFP-positive and Sox2-positive cells in the neuromasts of larvae treated with SP600125. (E) Quantification of the number of hair cells in control and SP600125-treated larvae at 24 hours and 48 hours after neomycin incubation. (F) Quantification of replicating cells in control and SP600125-treated larvae at 24 hours and 48 hours after neomycin incubation. (G) Quantification of the number of Sox2-positive cells in control and SP600125-treated larvae at 24 hours and 48 hours after neomycin incubation. In the 24-hour group, n = 100 control neuromasts, n = 40 5 μM SP600125-treated neuromasts, n = 60 10 μM SP600125-treated neuromasts, and n = 32 15 μM SP600125-treated neuromasts. In the 48-hour group, n = 72 control neuromasts, n = 28 5 μM SP600125-treated neuromasts, n = 32 10 μM SP600125-treated neuromasts, and n = 32 15 μM SP600125-treated neuromasts. *p < 0.05. (24-hour group: One-way ANOVA; GFP+ cells: F3, 228 =71.15, p < 0.05; Sox2+ cells: F3, 228 = 38.48, p < 0.05; BrdU+ cells: F3, 228 = 172.5, p < 0.05. 48-hour group: One-way ANOVA; GFP+ cells: F3, 160 = 184.9, p < 0.05; Sox2+ cells: F3, 160 = 90.65, p < 0.05; BrdU+ cells: F3, 160 = 365.5, p < 0.05). Bars are mean ± s.e.m. (H, I) Quantification of the ratio of BrdU-positive hair cells and the ratio of BrdU-positive supporting cells in control and SP600125-treated larvae at 24 hours and 48 hours after neomycin incubation. Bars are mean ± s.e.m. In the 24-hour group, n = 100 control neuromasts and n = 60 10 μM SP600125-treated neuromasts. In the 48-hour group, n = 72 control neuromasts and n = 32 10 μM SP600125-treated neuromasts. **p < 0.001. (24-hour group: BrdU+ HCs: unpaired t test, two-tailed, t = 11.54 , df = 158, p < 0.001; BrdU+ SCs: unpaired t test, two-tailed, t = 10.5, df = 158, p < 0.001. 48-hour group: BrdU+ HCs: unpaired t test, two-tailed, t = 16.74, df = 102, p < 0.001; BrdU+ SCs: unpaired t test, two-tailed, t = 4.922, df = 102, p < 0.001). Bars are mean ± s.e.m. |
|
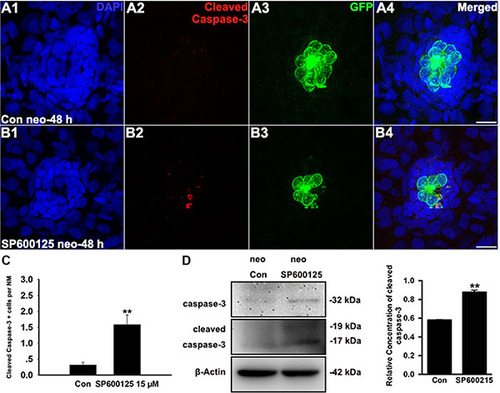
SP600125 induces apoptosis in neuromasts. (A–B) Cleaved caspase-3 staining in the neuromast from a control larva (A) and 15 μM SP600125-treated larvae (B). Scale bar = 10 μm. (C) SP600125 treatment increased the numbers of cleaved caspase-3-positive cells. Bars are mean ± s.e.m. n = 48 control neuromasts and n = 48 15 μM SP600125-treated neuromasts. **p < 0.001. (unpaired t test, two-tailed, t = 4.051, df = 94, p < 0.001). (D) After treatment of larvae with 15 μM SP600125 for 48 h, protein extracts were prepared and subjected to western blot assay using antibodies against caspase-3 and cleaved caspase-3. β-Actin was included as the loading control. |
|
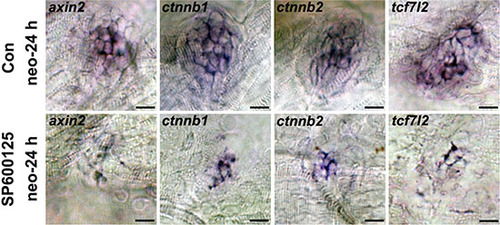
In situ hybridization of Wnt pathway-related genes in SP600125-treated and untreated larvae at 24 h after neomycin treatment. Expression of axin2, ctnnb1, ctnnb2, and tcf7l2 is significantly decreased in SP600125-treated neuromasts during the regeneration period. (axin2: n = 28 neuromasts from control animals, n = 20 neuromasts from SP600125-treated larvae; ctnnb1: n = 20 neuromasts from control animals, n = 16 neuromasts from SP600125-treated larvae; ctnnb2: n = 18 neuromasts from control animals, n = 16 neuromasts from SP600125-treated larvae; tcf7l2: n = 22 neuromasts from control animals, n = 20 neuromasts from SP600125-treated larvae). Results from one representative neuromast are shown. Scale bar = 10 μm. |
|
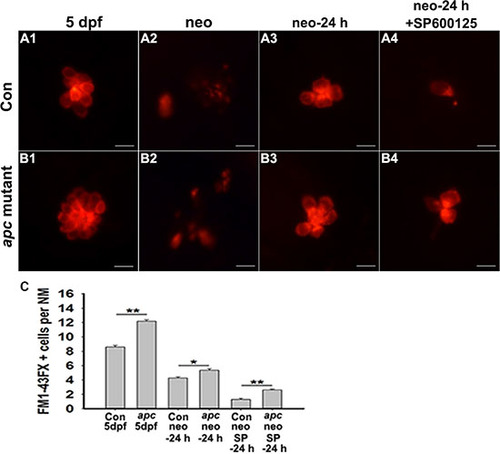
Decreased hair cell regeneration in JNK inhibition zebrafish can be partly rescued by over-activating Wnt signalling. (A–B) The FM1-43FX labelled hair cells are significantly increased in apc mutant zebrafish compared to control larvae in SP600125-treated and untreated larvae at 24 h after neomycin treatment. Scale bar = 10 μm. (C) Quantification of FM1-43FX-positive hair cells. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.001. (n = 53 neuromasts from the non-neomycin-treated 5 dpf control animals, n = 44 neuromasts from the non-neomycin-treated apc mutant zebrafish at 5 dpf, n = 72 neuromasts from the control larvae at 24 h following neomycin damage, n = 11 neuromasts from apc mutant larvae at 24 h following neomycin damage, n = 21 neuromasts from 15 μM SP600125-treated larvae at 24 h following neomycin damage, n = 63 neuromasts from 15 μM SP600125-treated apc mutant larvae at 24 h following neomycin damage. Con 5 dpf vs. apc mutant 5 dpf: unpaired t test, two-tailed, t = 11.39, df = 95, p < 0.001; Con neo-24 h vs. apc neo-24 h: unpaired t test, two-tailed, t = 2.767, df = 81, p = 0.007; Con neo SP600125-24 h vs. apc neo SP600125-24 h: unpaired t test, two-tailed, t = 5.186, df = 82, p < 0.0001). |
|
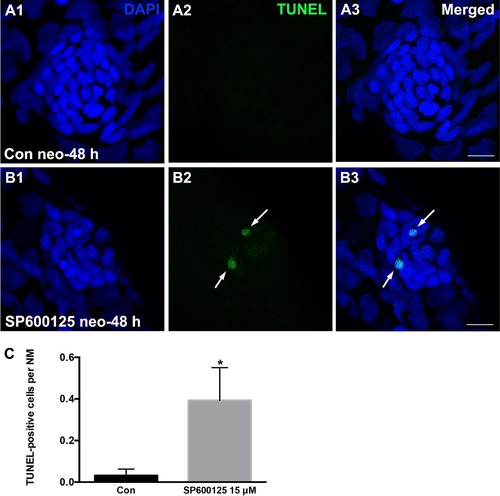
SP600125 induces apoptosis in neuromasts. (A–B) TUNEL staining in the neuromasts of control and SP600125 (15 μM)-treated larva at 48 h following neomycin-induced hair cell death. White arrows indicate TUNEL-positive cells. Scale bar = 10 μm. (C) Quantification of apoptosis induced by SP600125 treatment. Data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m, *p < 0.05. (n = 32 neuromasts from control animals, n = 28 neuromasts from 15 μM SP600125-treated animals; unpaired t test, two-tailed, t = 2.401, df = 58, p = 0.0196). |
|
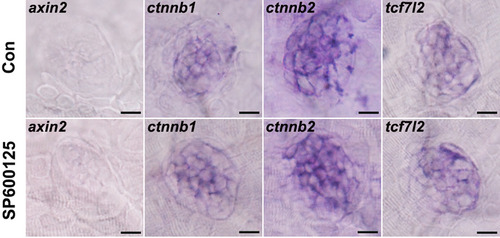
Effect of SP600125 on Wnt pathway-related gene expression in neuromasts. Expression of axin2, ctnnb1, ctnnb2, and tcf7l2 in SP600125-treated (24 h) and untreated control larvae without neomycin treatment. (axin2: n = 26 neuromasts from control animals, n = 30 neuromasts from SP600125-treated larvae; ctnnb1: n = 36 neuromasts from control animals, n = 28 neuromasts from SP600125-treated larvae; ctnnb2: n = 32 neuromasts from control animals, n = 34 neuromasts from SP600125-treated larvae; tcf7l2: n = 24 neuromasts from control animals, n = 24 neuromasts from SP600125-treated larvae). Results from one representative neuromast are shown. Scale bar = 10 μm. |
|
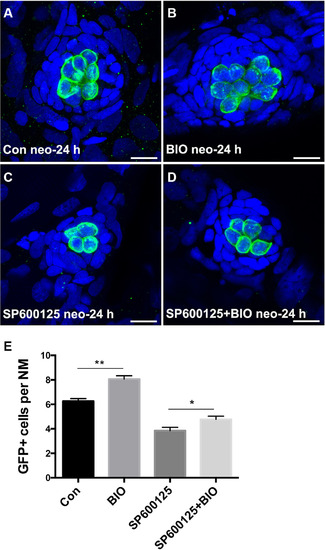
Decreased hair cell regeneration in JNK inhibition zebrafish can be partly rescued by BIO treatment. (A–D) BIO/SP600125-treated larvae had signifi cantly more GFP-positive hair cells in neuromasts when compared with SP600125-treated animals at 24 h after neomycin treatment. Scale bar = 10 μm. (E) Quantification of GFP-positive hair cells. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.001. (n = 38 neuromasts from control animals, n = 31 1 μM BIO-treated neuromasts, n = 34 10 μM SP600125-treated neuromasts, n = 31 SP600125/BIO-treated neuromasts. Con vs. SP600125: unpaired t test, two-tailed, t = 7.229, df = 70, p < 0.0001; Con vs. BIO: unpaired t test, two-tailed, t = 5.359, df = 67, p < 0.0001; SP600125 vs. BIO: unpaired t test, two-tailed, t = 10.99, df = 63, p < 0.0001; SP600125 vs. BIO+SP600125: unpaired t test, two-tailed, t = 2.456, df = 63, p = 0.0168; BIO+SP600125 vs. Con: unpaired t test, two-tailed, t = 4.545, df = 67, p < 0.0001). |