- Title
-
csrnp1a Is Necessary for the Development of Primitive Hematopoiesis Progenitors in Zebrafish
- Authors
- Espina, J., Feijoo, C.G., Solis, C., and Glavic, A.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
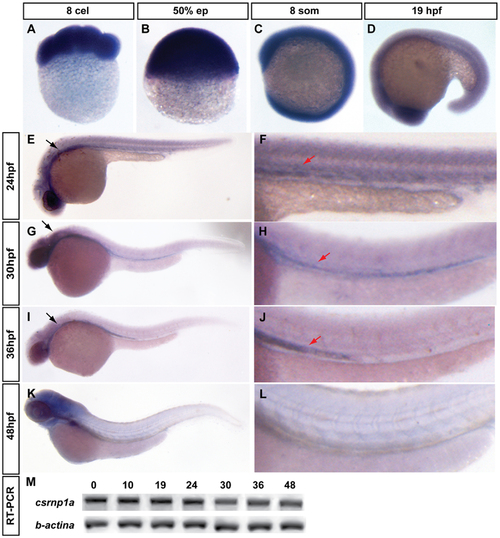
Expression pattern of csrnp1a in zebrafish embryonic development. Early embryos show a ubiquitous signal of csrnp1a (A to D). Latter Stages (E to L) show an extensive anterior expression in the head region (black arrow) and a caudal, much localized expression, at the intermediate cell mass (ICM) (red arrow) (all are lateral views; A to C animal pole to the top; D to L anterior to the left). (F, H, J, L) Magnifications showing the expression of csrnp1a at ICM. Note the dynamic extension and retraction of its expression. (M) csrnp1a RT-PCR; the numbers above the gel correspond to developmental stages (as hpf). |
|
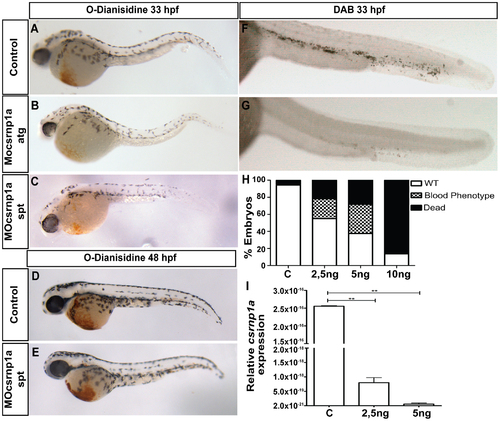
csrnp1a knockdown decreases the number of blood cells in circulation. O-Dianisidine stain labels erythrocytes (A, B, C, D, E) and Diaminobenzidine (DAB) blood cells in general at the ICM (F and G). The injection of csrnp1a morpholino produces a dramatic reduction of blood cells in 34% of the injected embryos (n = 16/47) at 33 hpf (A, B, C, F, G) which is reverted at 48 hpf (D, E) (all are lateral views, anterior to the left). (H) Chart summarizing the morpholino dose-phenotype quantifications of 26 hpf control embryos (n = 71) and injected with 2,5 ng (n = 69), 5 ng (n = 85) or 10 ng (n = 87) of Mocsrnp1a spt morpholino. (I) qPCR with primers located in exon 2 and 3 of 24 hpf control embryos (C) and splicing morphants injected with two concentrations, 2,5 and 5 ng per embryo, showing the relative expression of csrnp1a message, which decreases significantly in a dose-dependent manner (t student p<0,01). |
|
Csrnp1a reduction does not affect csrnp1 expression, but has redundant function in the appearance of circulating blood cells. RT-PCR against csrnp1 message in control and csrnp1a morphant embryos (A) showing no differences in the csrnp1 expression at 24 and 30 hpf at the Mocsrnp1a spt concentration used. (B to E) O-dianisidine stain showing the decrease in blood cells in 38,7% of csrnp1a injected embryos (C); 22,6% of the csrnp1 morphant embryos (D), and 64,4% when csrnp1 and csrnp1a morpholino are co-injected (E). |
|
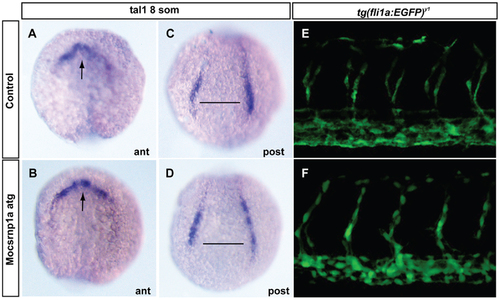
Csrnp1a reduction does not affect the hemato-angiogenic mesoderm. In situ hybridization indicating the expression of the hemangioblast marker, tal1/scl at 8 somites (A to D) (A, B anterior view; C, D posterior view). Control and morphant 32 hpf transgenic zebrafish embryos expressing GFP under the promoter of the endothelial marker fli1a (Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1)(E, F) (lateral view, anterior to the left). We did not observe difference in either marker in 100% of the injected embryos (n = 53). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
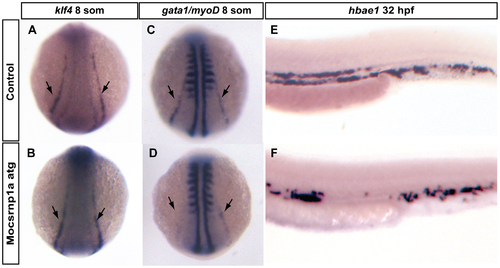
Erythroid/Gata1 precursors are affected by csrnp1a knockdown. (A, C, E) Control and (B, D, F) morphant embryos. At 8 somite stage the expression of the erythroid marker klf4 was not affected in morphant embryos (A, B) (100%, n = 48). However a clear decrease in gata1 expression was detected in csrnp1a deficient embryos (compare C with D) (54,8%; n = 23/42) without major changes in the number of myoD stripes (7,1%; n = 3/42, more than 2 stripes), which served as readout of developmental progression. Control embryos showed normal gata1 expression in 100% of the cases (n = 0/27) and 3,7% have altered myoD expression (n = 1/27). In agreement with gata1 inhibition, at 32 hpf terminal differentiation marker, hbae1, was reduced in morphant embryos (E, F) (32,6%; n = 14/43). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
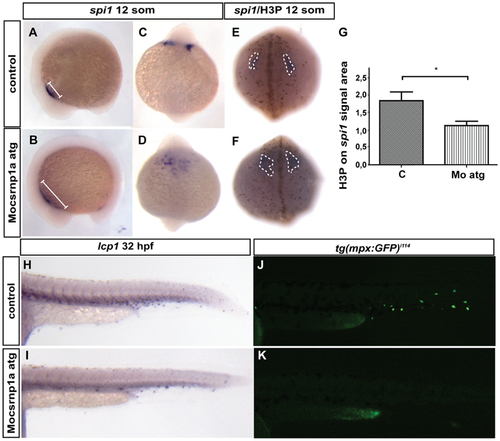
Myeloid lineage is affected by csrnp1a knockdown. Morphants embryos show an alteration in the spi1 signal (A to D; A, B lateral views anterior lo left; and D, E anterior views). 85,7% of control embryos exhibit normal spi1 expression pattern (n = 42/49) (A, C), while csrnp1a morphants exhibit altered spi1 expression in 59,2% (n = 61/103) (B, D). The spi1 changes are accompanied by a significant decrease in proliferation (showed as the number of H3P within the spi1 signal area) (E, F, and G). Finally, a decrease in the macrophage specific marker lcp1 (43,8%; n = 14/32) is evidenced by ISH (H, I), and a clear reduction in the neutrophil specific marker mpo is evident in the transgenic line expressing GFP under the mpo promoter Tg(Bacmpo:GFP)i114 (J, K)(47,2%; n = 25/53). All are lateral views, anterior to the left. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
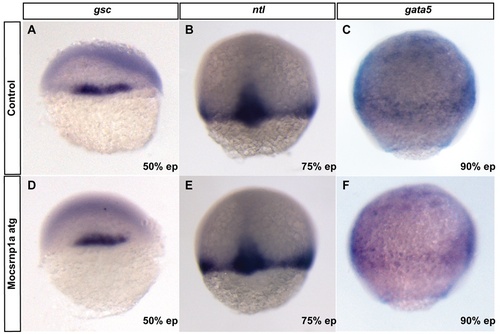
Early mesoderm specification is not altered in csrnp1a knockdown condition. Expression of the mesodermal markers goosecoid (gsc) (A, D), notail (ntl) (B, E) and gata5 (C, F) detected by ISH at three different stages of gastrulation. No differences were detected between morphant and control embryos (100%, n = 37, 49 and 46 embryos respectively). |
|
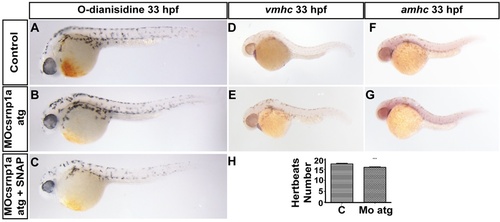
csrnp1a knockdown does not affect blood flow. Morphant embryos were incubated in the vasodilator SNAP, and its ability to rescue the reduction of blood cells was analyzed (A, B, C). csrnp1a knockdown phenotype was not rescue by SNAP treatment. (A) Control 100% n = 53; (B) Mo csrnp1a atg 36,8% n = 21/57 of morphant phenotype; (C) Mocsrnp1a atg incubated with SNAP 33,9% n = 21/62 of morphant phenotype. In situ hybridizations against ventricular (vmhc) (D, E) and auricular (amhc) (F, G) markers show that injected embryos have normal heart development (100%; n = 43; n = 45 respectively). All are lateral views, anterior to the left. (H) Chart depicting the number of heartbeat in 10 seconds in control and csrnp1a morphant embryos. |
|
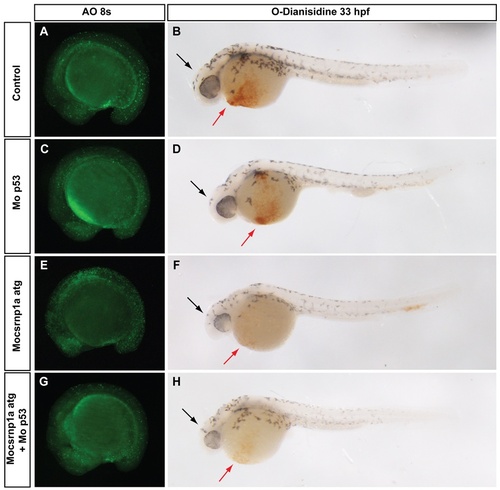
csrnp1a morphants exhibit an increase in cell death due to morpholino toxicity which is not responsible for the reduction in blood cells in circulation. We analyzed cell death by acridine orange in embryos injected with control morpholino (A), csrnp1a morpholino (C), p53 morpholino (E), or a mixture of csrnp1a and p53 morpholinos (G). A clear increased in cell death is detected in csrnp1a morphant embryos (86,7%; n = 58/67), which is reversed by p53 co-injection (16,7%; n = 16/96). The cell blood phenotype was screened at 33 hpf using O-Dianisidine stain in (B) control, (D) csrnp1a, (F) p53 morphant embryos and in embryos co-injected with both morpholinos (H). The csrnp1a, p53 co-injected embryos (H; 39,6% n = 21/53) have the same penetrance of the blood phenotype as csrnp1a morphants (F; 35,7% n = 15/42) (red arrows). It worth mention that the slight head reduction exhibited by csrnp1a morphant embryos was also detected in co-injected embryos (black arrows). All are lateral views, anterior to the left. |