- Title
-
Hmx4 regulates Sonic hedgehog signaling through control of retinoic acid synthesis during forebrain patterning
- Authors
- Gongal, P.A., March, L.D., Holly, V.L., Pillay, L.M., Berry-Wynne, K.M., Kagechika, H., and Waskiewicz, A.J.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
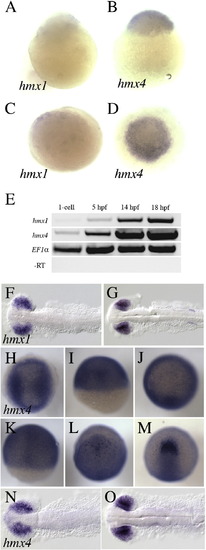
hmx1 and hmx4 expression during early zebrafish development. hmx1 is not detectable in 1-cell embryos by in situ hybridization (lateral view in A; dorsal view in C), while robust expression of hmx4 is detected (lateral view in B; dorsal view in D). hmx1 transcript can be weakly detected by RT-PCR at 5 hpf, and becomes robust at 14–18 hpf (E), when it is strongly expressed in the eye and otic vesicle (F–G). hmx4 transcript can be detected at the 1-cell stage by RT-PCR, and is robustly expressed from 0 to 18 hpf (E). hmx4 transcript is broadly distributed from 0 to 10 hpf, and is slightly enriched at the dorsal midline during gastrulation (K). After gastrulation is complete, hmx4 is strongly expressed in the eye field (M), and at 14–18 hpf, in retina progenitors (N–O). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
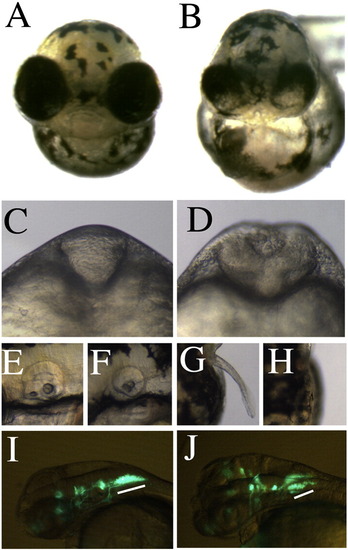
Hmx4 deficient embryos have a narrowed eye field and open neural tube. (A–B) hmx4 morphants have a strongly narrowed eye field, shown at 3 dpf. (C–D) The neural tube fails to close in hmx4 morphants, shown at 18 hpf. hmx4 morphants have (E–F) small otic vesicles, (G–H) a loss of pectoral fins, and (I–J) a reduction in vagal motor neurons (underlined in white), assessed in the Tg(isl1:gfp) line at 3 dpf. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
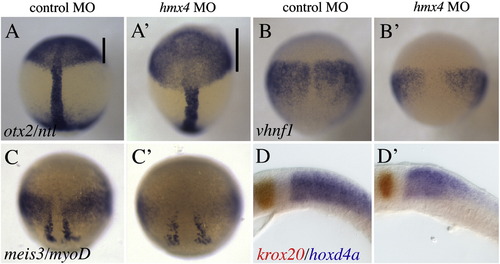
hmx4 morphants have defects in RA signaling. (A) otx2 is expanded in hmx4 morphants (extent of domain marked by the black line), while vhnf1 (B) and meis3 (C) are reduced in hmx4 morphants at 90% epiboly. (D) hoxd4a (blue) in 10s hmx4 morphants is reduced, while krox20 (red) expression in r3 and r5 is unchanged. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
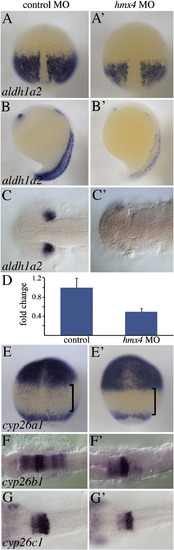
hmx4 morphants have disrupted RA metabolism gene expression. aldh1a2 is reduced in the paraxial mesoderm of hmx4 morphants at 90% epiboly (A), and in the somites (B) and dorsal optic vesicle (C) at 18 hpf. (D) qPCR showing the significantly reduced levels of aldh1a2 transcription in hmx4 morphants (see text for statistical tests), with the levels in wild type embryos set to 1. Error bars indicate standard deviation. (E) cyp26a1 is mildly expanded towards the posterior in hmx4 morphants, and abolished in the presumptive hindbrain domain (bracket). In hmx4 morphants, the r6-7 domain of cyp26b1 is abolished (F), while the r3-r4 domain of cyp26c1 is not affected (G). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
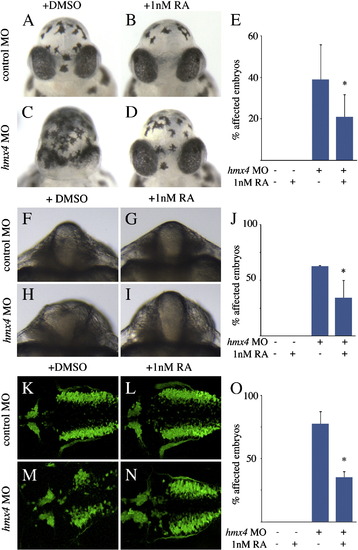
RA rescues hmx4 morphant phenotypes. Eye field narrowing (A–D), the neural tube closure defect (F–I), and loss of vagal motor neurons (K–N) in hmx4 morphants are rescued by treatment with 1 nM RA. Frequencies of morphant phenotypes are scored for eye field narrowing (E), open neural tube (J) and loss of vagal motor neurons (O). All rescues are statistically significant (see text for statistical tests). Error bars represent standard error. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
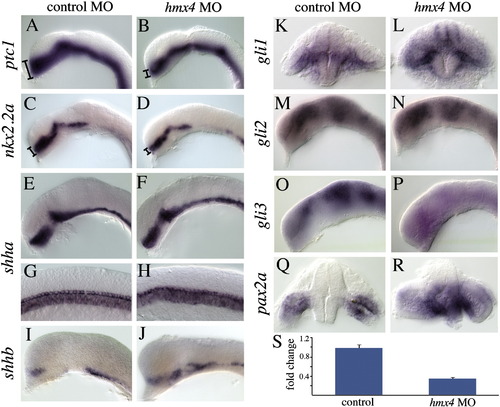
hmx4 deficiency causes defects in Shh signaling. The Shh target genes ptc1 (A–B) and nkx2.2a (C–D) are reduced in 18 hpf hmx4 morphants. Dorsal–ventral extents of expression are denoted by the bracket. shha expression is unaffected in the forebrain (E–F), notochord and floor plate (G–H) in hmx4 morphant embryos. (I–J) shhb expression is upregulated in the ventral floor plate of hmx4 morphants. Sections through the forebrain reveal that hmx4 morphants have a dorsal expansion of gli1 expression (K–L). gli2 expression is unchanged in morphants (M–N), while gli3 expression is strongly reduced (O–P). Sections through the forebrain reveal that pax2a is expanded throughout the forebrain of hmx4 morphants (Q–R). (S) qPCR showing the significantly reduced relative levels of gli3 transcription in hmx4 morphants, with the levels in wild type embryos set to 1 (see text for statistical tests). Error bars indicate standard deviation. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
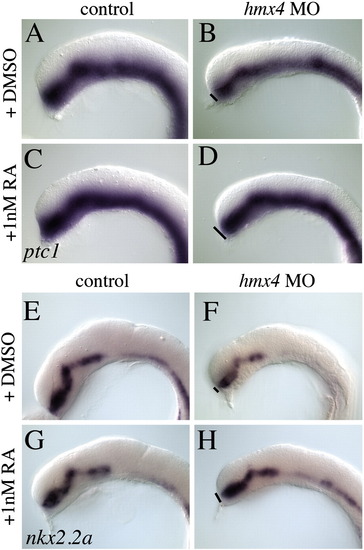
Shh signaling defects in hmx4 morphants are rescued by RA. 18 hpf hmx4 morphants show a reduction of ptc1 (A–D) and nkx2.2a (E–H) that are significantly rescued by RA treatment (see text for frequencies and statistical tests). Black lines indicate the size of gene expression domains on the dorsal–ventral axis, for comparison of control hmx4 morphants and RA-treated hmx4 morphants. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
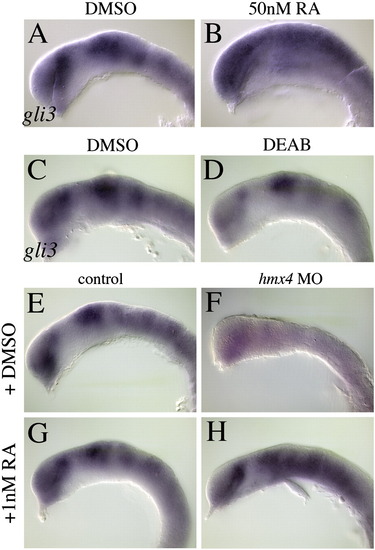
Retinoic acid regulates gli3 transcription and rescues gli3 levels in hmx4 morphants. Treatment with RA induces gli3 expression throughout the forebrain (A–B) of 18 hpf embryos, while inhibiting RA synthesis with DEAB causes its reduction (C–D). (E–H) hmx4 morphants have reduced gli3 expression, which is significantly rescued by RA treatment (see text for frequencies and statistical tests). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
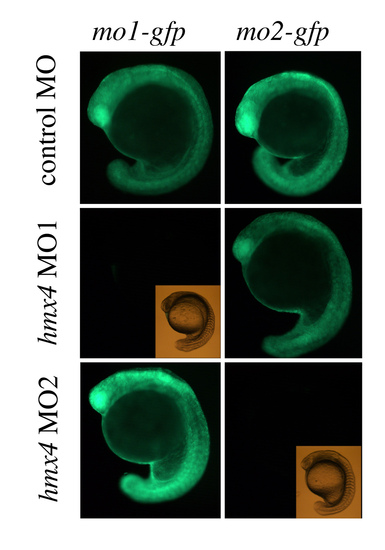
hmx4 morpholinos are specific Each hmx4 MO specifically knocks down translation of eGFP RNA linked to its specific target sequence, but not eGFP linked to a non-complementary target sequence. |
|
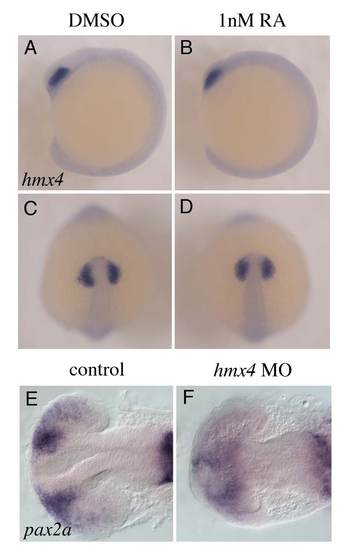
hmx4 is not induced by low doses of RA Treatment with the lose dose of RA used for rescue experiments does not induce hmx4 expression (lateral view in B, dorsal view in D), compared with DMSO controls (lateral view in A, dorsal view in C) at 10s. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 355(1), Gongal, P.A., March, L.D., Holly, V.L., Pillay, L.M., Berry-Wynne, K.M., Kagechika, H., and Waskiewicz, A.J., Hmx4 regulates Sonic hedgehog signaling through control of retinoic acid synthesis during forebrain patterning, 55-64, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.