Fig. 1
|
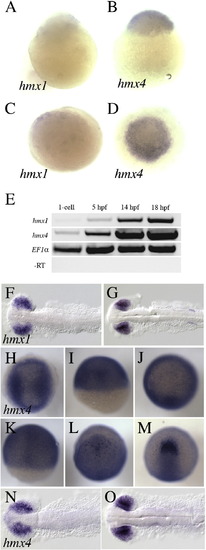
hmx1 and hmx4 expression during early zebrafish development. hmx1 is not detectable in 1-cell embryos by in situ hybridization (lateral view in A; dorsal view in C), while robust expression of hmx4 is detected (lateral view in B; dorsal view in D). hmx1 transcript can be weakly detected by RT-PCR at 5 hpf, and becomes robust at 14–18 hpf (E), when it is strongly expressed in the eye and otic vesicle (F–G). hmx4 transcript can be detected at the 1-cell stage by RT-PCR, and is robustly expressed from 0 to 18 hpf (E). hmx4 transcript is broadly distributed from 0 to 10 hpf, and is slightly enriched at the dorsal midline during gastrulation (K). After gastrulation is complete, hmx4 is strongly expressed in the eye field (M), and at 14–18 hpf, in retina progenitors (N–O). |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | 1-cell to 14-19 somites |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 355(1), Gongal, P.A., March, L.D., Holly, V.L., Pillay, L.M., Berry-Wynne, K.M., Kagechika, H., and Waskiewicz, A.J., Hmx4 regulates Sonic hedgehog signaling through control of retinoic acid synthesis during forebrain patterning, 55-64, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.