- Title
-
Epidermal transient down-regulation of retinol-binding protein 4 and mirror expression of apolipoprotein Eb and estrogen receptor 2a during zebrafish fin and scale development
- Authors
- Tingaud-Sequeira, A., Forgue, J., Andre, M., and Babin, P.J.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
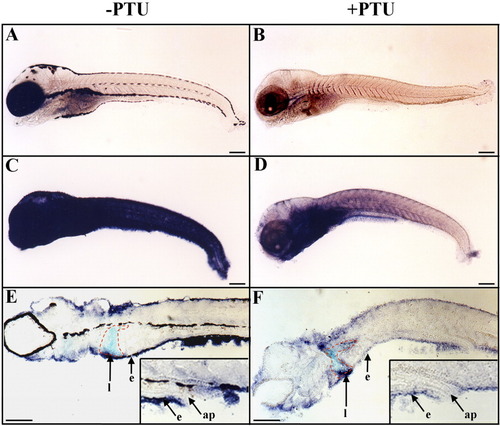
Epidermal expression of rbp4 is down-regulated following treatment with PTU (1-phenyl-2-thio-urea). A-F: Embryos and larvae were raised, from fertilization to 10 days postfertilization (dpf), in water without (A,C,E) or with (B,D,F) added PTU to prevent pigment formation. A-F: Whole-mount in situ hybridizations are shown in lateral views and anterior to the left with digoxigenin-labeled sense (A,B) and antisense (C-F) rbp4 riboprobes. E,F: Parasagittal sections after whole-mount in situ hybridization. C-F: Epidermal rbp4 transcript hybridization signal was strongly reduced in the epidermis of PTU-treated larva (D,F) in comparison with untreated animals (C,E). E,F: The outline of the liver is traced in red. Inserts in E and F are enlarged views of the anal papilla region. e, epidermis; l, liver; ap, anal papilla. Scale bars = 250 μm. |
|
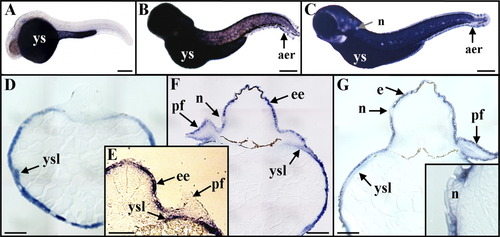
Expression of rbp4 during zebrafish embryonic and early larval development. A-C: Whole-mount in situ hybridizations, by using digoxigenin-labeled antisense riboprobes, are shown in lateral views and anterior to the left at 24 hours postfertilization (hpf; A), 48 hpf (B), and 72 hpf (C). D-G: Transverse sections after in situ hybridizations at 24 hpf (D), 42 hpf (E), 48 hpf (F), and 72 hpf (G). A: By 24 hpf, rbp4 hybridization signal was found in the yolk sac. D: Histological sections demonstrated that rbp4 transcripts were restricted to the yolk syncytial layer. E: By 42 hpf, an epidermal expression of rbp4 began, but no transcripts were detected in pectoral fin-bud epidermis. B,C,F,G: By 48 hpf (B,F) and 72 hpf (C,G, and insert), rbp4 transcripts were detected in the embryonic epidermis, in pectoral fin-bud epidermis, in the yolk syncytial layer, in dorsal and ventral apical ectodermal ridges, but not in neuromasts. aer, apical ectodermal ridge; e, epidermis; ee, embryonic epidermis; n, neuromast; tb, tail bud; pf, pectoral fin buds; ys, yolk sac; ysl, yolk syncytial layer. Scale bars = 200 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
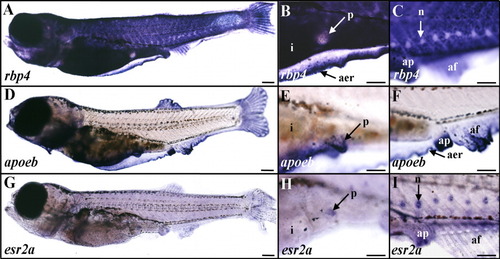
Expression of rbp4, apoeb, and esr2a in late zebrafish larva. A-C: rbp4. D-F: apoeb. G-I: esr2a. Whole-mount in situ hybridizations are shown in lateral views and anterior to the left with digoxigenin-labeled antisense riboprobes of 25-30 days postfertilization (dpf; 5.5-6 mm long) larvae. B,E,H and C,F,I are enlarged views of the pelvic fin-bud and anal papilla regions, respectively. A-C: rbp4 expression was detected in the epidermis and the apical ectodermal ridge (A,B), but not in pelvic fin buds (A,B) or neuromasts (C). D-F: apoeb transcripts were strongly expressed in pelvic fin buds (D,E) and the hybridization signal was detected in the apical ectodermal ridge, anal papilla, and elongating unpaired fin folds (D,F). G-I: esr2a transcripts were expressed in a diffuse manner in the epidermis (G-I), and in pelvic fin buds (H), and a strong signal was detected in neuromasts (I). af, anal fin; ap, anal papilla; apical ectodermal ridge, aer; i, intestine; n, neuromast; p, pelvic fin bud. Scale bars = 300 μm in A,D,G, 150 μm in B,C,E,F,H,I. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
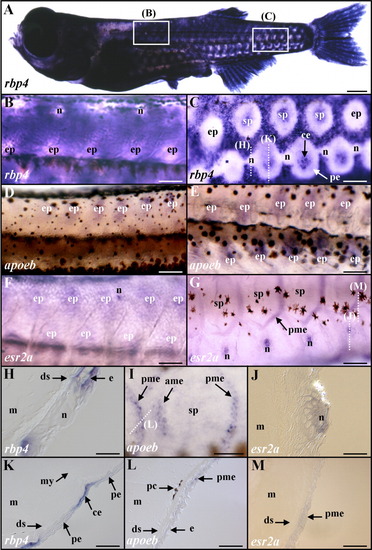
Expression of rbp4, apoeb, and esr2a during the zebrafish larval-juvenile transition. A-C,H,K: rbp4. D,E,I,L: apoeb. F,G,J,M: esr2a. Whole-mount in situ hybridizations (A-G,I) and histological sections after in situ hybridizations (H,J-M) of 35-40 days postfertilization (dpf, around 8.5 mm long) larvae hybridized with digoxigenin-labeled antisense riboprobes. Section planes of H,J-M are indicated by white dotted lines in C,G,I. A-C: rbp4 transcripts were detected in the larval skin (A), and their expression was initially down-regulated in scale epidermal placodes, as shown in enlarged views from the anterior (B) and posterior (C) regions of the trunk. B,C,H,K: rbp4 expression was located in basal epidermal cells (H,K) but not neuromasts (B,C,H). C,K: After this initial down-regulation in the placode field (peripheral epidermal placodes in C), the rbp4 transcript signal was then detected in the central epidermis of scale papillae (C,K; central scale papillae in C). The process was initiated around the initiator squamation locus in epidermal placodes in the midline rows of the caudal peduncle and spread from scale to scale papillae. As a consequence, nascent scale papillae were observed at different stages of development according to their position on each side of the body in relation to the initiator squamation locus. C: Within a scale papilla, the rbp4 hybridization signal gradually invaded the peripheral epidermis of the nonoverlapping scale papillae. D-F: Mirroring the down-regulation of rbp4 expression, apoeb (D,E) and esr2a (F) induction was observed, leading to imbricated rows of expressing epidermal placodes. B,D,F and C,E are gene expression patterns depicted at a similar early and late developmental stage of the scale papilla, respectively. F,G,J: A moderate esr2a hybridization signal was also observed in the epidermis covering the whole larva (F,G) and a very strong signal in the neuromasts (F,G,J). G,I,L,M: apoeb transcripts were then restricted to the anterior and posterior margin epidermis, mostly in their basal cell layer (I,L) and were subsequently restricted to the posterior margin epidermis of the scale papilla (data not shown), a pattern also observed with esr2a (G,M). ame, anterior margin epidermis of the scale papilla; ce, central epidermis of the scale papilla; ds, dermal stroma; ep, epidermal placode; m, muscle cells; my, myoseptum; n, neuromast; pc, pigments cells located within the hypodermis between dermis and muscles; pe, peripheral epidermis of the scale papilla; pme, posterior margin epidermis of the scale papilla; sp, scale papilla. Scale bars = 500 μm in A, 100 μm in B-G,I, and 20 μm in H,J-M. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
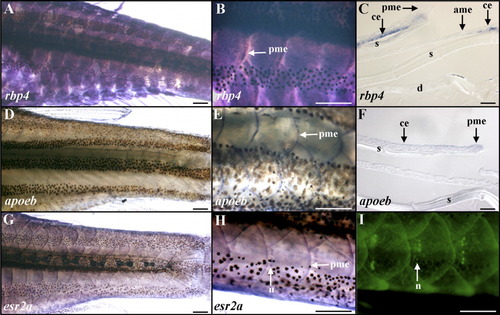
Epidermal expression of rbp4, apoeb, and esr2a in adult zebrafish. A-C: rbp4. D-F: apoeb. G-I: esr2a. A-I: Whole-mount in situ hybridizations with digoxigenin-labeled antisense riboprobes (A,B,D,E,G,H), histological sections after in situ hybridizations (C,F), or in vivo labeling with the fluorescent vital dye 4-di-2-Asp (I) are shown in lateral views and anterior to the left. C,F: Spaces observed between epidermis, scale, and dermis are sectioning artifacts. A,B: Uniform rbp4 hybridization signal distribution is observed in the epidermis of overlapping scales. C: rbp4 is expressed in the basal layer of the epidermis with no signal in epidermal cells covering the anterior and posterior margin regions of the formed scale. D-H: apoeb (D-F) and esr2a (G,H) transcripts are colocalized in the posterior margin epidermis of the scale. G,H: A moderate esr2a hybridization signal is observed in the epidermis covering the whole animal. H: Secondary neuromasts of the lateral lines identified by labeling their hair cells using 4-di-2-Asp (I) express esr2a. ame, anterior margin epidermis of the scale; ce, central epidermis of the scale; d, dermis; n, neuromast; pme, posterior margin epidermis of the scale; s, scale. Scale bars = 500 μm in A,B,D,E,G-I, 20 μm in C,F. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|