- Title
-
The Metalloproteinase adam19b Is Required for Sensory Axon Guidance in the Hindbrain
- Authors
- Cox, J.A., Voigt, M.M.
- Source
- Full text @ Front. Neural Circuits
|
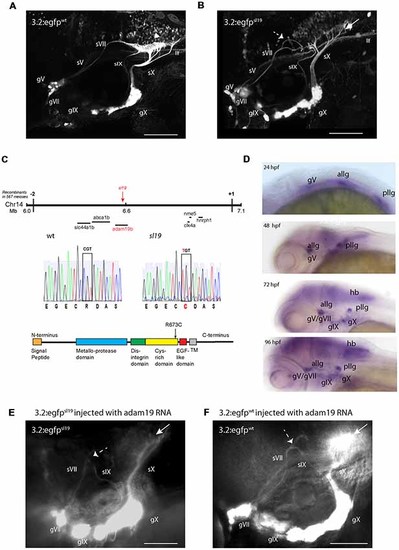
Characterization of the sl19 mutant line. (A) Wild type larva at 4 days post fertilization (4 dpf) showing normal pattern of cranial sensory ganglia (CSG) projections. sV (also llf-lateral longitudinal fascicle), sVII, sIX and sX are the projections of the trigeminal (gV), facial (VII), glossopharyngeal (IX) and vagus (X) ganglia, respectively. White arrowhead shows normal hindbrain plexus, where sVII, sIX and sX sensory axons terminate. (B) CSG projections in a 4dpf sl19 mutant. White arrow indicates malformed hindbrain plexus and dotted arrow shows the misrouted and defasciculated sVII failing to terminate in the plexus. sIX and sX fail to form normal terminal fields. Projections from gV appear normal. (C) Positional cloning of sl19. The lesion was mapped to a critical region on chromosome 14 between 6 and 7 Mb. Transcripts of all genes in this region (20 in total) were sequenced (for clarity, only some of these genes are shown in the Figure). Only the adam19b gene showed an altered coding sequence—a single base mutation in exon 17. This C > T conversion causes an arginine to cysteine switch at amino acid 673 in the cysteine-rich domain (CRD) of A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase (ADAM) 19b (CRD). (D) Wholemount in situ hybridization (ISH) of adam19b in the zebrafish head. At 24 hpf, adam19b is expressed in the trigeminal ganglion (gV), the anterior lateral line ganglion (allg) and the posterior lateral line ganglion (pllg). At 48 hpf, expression has expanded to include regions of the hindbrain. By 72 hpf, adam19b is also expressed in the epibranchial ganglia (gVII, gIX and gX) and in the hindbrain (hb); by 96 hpf, expression has increased in all these cranial structures. Sense probe did not produce staining at any time point (data not shown). (E) adam19b full length RNA injected into sl19 mutant. Over-expression of adam19b did not rescue the mutant phenotype, but resulted in a higher incidence of the mutant phenotype (see text). White arrow indicates malformed plexus; dotted arrow shows misrouted sVII and sIX. (F) adam19b full length RNA injected into wild type. As can be seen, over-expression of adam19b induced aberrant epibranchial projections in 4 dpf wild type fish, identical to that found in the sl19mutant. White arrow: malformed plexus, showing how sX forms a dense clump of axons, instead of the organized branching of the axons seen in un-injected controls (A). Dotted arrow: misrouted sVII and sIX. Panels (A,B) are confocal z-stacks, panels (E,F) are epifluorescent micrographs. All images are oriented anterior to the left and dorsal at top. Scale bars = 100 μm. |
|
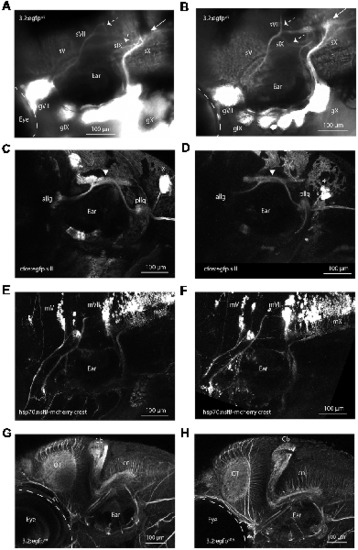
Validation of adam19b as critical for epibranchial sensory axon pathfinding. (A) adam19b start morpholino (MO1; 4 ng) injected into Tg(p2rx3.2:gfp) embryos. This image shows the disruption of the projections of sVII and sIX (dotted arrows) and the malformed plexus (white arrow), recapitulating the phenotype of sl19. sV appears unaffected. A 5 bp-mismatched MO gave no phenotype (for image of control fish, see Figure 1A). (B) Phenotype from CRISPR targeting of adam19b exon 2. White arrow shows malformed plexus and dotted arrows show disrupted axon projections of the sVII and sIX, again phenocopying sl19 (for image of control fish, see Figure 1A). Injection of gRNAs targeting other genes (e.g., drg11, golden) did not produce these phenotypes). sVII, sIX and sX are the projections of the facial (gVII), glossopharyngeal (gIX) and vagus (gX) ganglia, respectively. (C) Confocal image of 4 dpf Tg(3.2:nsfB-mcherry/cfos:gfp.sill) wild-type larvae, showing the anterior lateral line ganglia (allg) and the posterior lateral line ganglia [pllg; green fluorescent protein (gfp) channel: cfos:gfp.sill), which project to the lateral line plexus (white arrowhead) in the hindbrain. (D) Confocal image of 4 dpf Tg(3.2:nsfB-mcherry/cfos:gfp.sill] adam19b CRISPR/Cas9 mutants demonstrating the lateral line projections to the hindbrain are not affected by the adam19b CRISPR indels (gfp channel: cfos:gfp.sill) *neuromasts. (E) Confocal image of banchiomotor nerves in 4 dpf wild-type Tg(3.2:gfp/hsp70:nsfB-mcherry.crest) larvae, showing the segmental organization of the motor neurons (mV, mVII and mX; red channel: hsp70:nsfB-mcherry.crest). (F) Confocal image of branchiomotor nerves in Tg(3.2:gfp/hsp70:nsfB-mcherry.crest). adam19b CRISPR/Cas9 mutants show that the segmental organization of the motor nuclei (mV, mVII and mX) and their projections appear normal (red channel: hsp70:nsfB-mcherry.crest). (G,H) The hindbrain organization is not affected in sl19 mutants. Anti-acetylated tubulin immunostaining of 4 dpf wild-type (G) and sl19 mutant larvae (H) shows no disruption to the cerebellum (Cb), the optic tectum (ot) or the commissural neurons (cn) in the mutants. For panels (C–F), cognate images in the channel showing epibranchial afferents are shown in Supplementary Figures S5, S6. All images are oriented anterior to the left and dorsal at top. Scale bars = 100 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
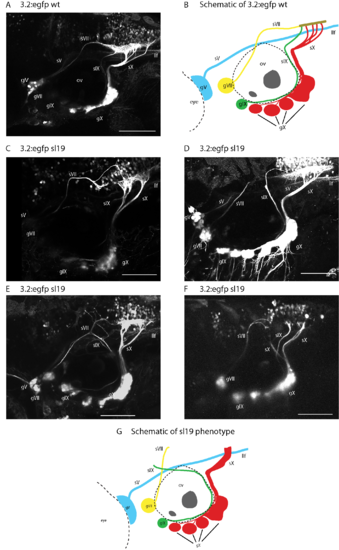
Variations in sl19 phenotype in Tg(p2rx3.2:gfp) embryos. sV (also labeled as llf), sVII, sIX and sX are the projections of the trigeminal (gV), facial (gVII), glossopharyngeal (gIX) and vagus (gX) ganglia, respectively. Panel (A) shows wild type p2rx3.2:gfp. Panel (B) is a schematic showing the ganglia and their projections in matching colors. Panels (C–F) are images from individual sl19 mutants. Panel (C) shows sVII defasciculating, with the majority of fibers stopping before reaching the plexus and the few fibers that do reach the plexus do so in an aberrant fashion. sIX joins sX before it enters the plexus, and sX shows aberrant branching. In (D), the main bundle of sIX stops in the hindbrain while a small number of fibers make a caudal turn towards the plexus. sX also shows a small degree of defasciculation by individual axons. Panel (E), sVII defasiculates and sIX continues in an anterior direction towards sVII. sX fails to branch properly but does contribute to the plexus. Panel (F), sVII again defasciculates and fails to reach the region of the plexus, sIX stops in the hindbrain and fails to form a terminal field, and sX shows abnormal branching and also fails to form a normal terminal field. Panel (G) is a schematic showing a selection of the aberrant phenotypes seen in sl19 mutants. All images are confocal z-stacks oriented anterior to the left and dorsal at top. Scale bars = 100 μm. |
|
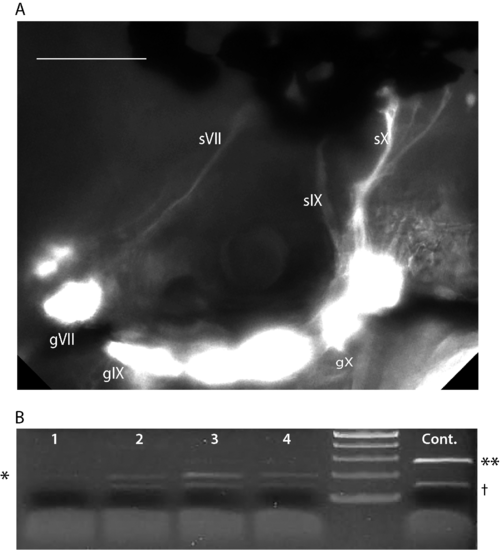
A second morpholino (MO2) was designed against the e17i17 splice junction resulting in an in-frame deletion of exon 17 (corresponding to aa 666–691), leading to disruption of the CRD (A; sequence shown in Supplementary Table S2). Injection of MO2 (4–8 ng/nL) into 3.2:gfp embryos resulted in mis-routing of the epibranchial projections, similar to MO1. sVII, sIX and sX are the projections of the facial (gVII), glossopharyngeal (gIX) and vagus (gX) ganglia, respectively. Note the disruption of sX afferents and lack of hindbrain plexus. All images are oriented anterior to the left and dorsal at top. Scale bars = 100 μm. (B) Verification of effectiveness of MO2. cDNA was synthesized from four 48 hpf embryos injected with MO2 and a control, uninjected 48 hpf embryo. Primers E16.F and E18.R were designed (see Supplementary Table S2) to amplify a 280 bp fragment in control embryos (last lane on right, **). In MO2 injected embryos (lanes 1–4), a 200 bp fragment (*) was amplified, indicating a loss of exon 17 (80 bp). There is a non-specific PCR artifact at 150 bp (†), which appears in all reactions. |
|
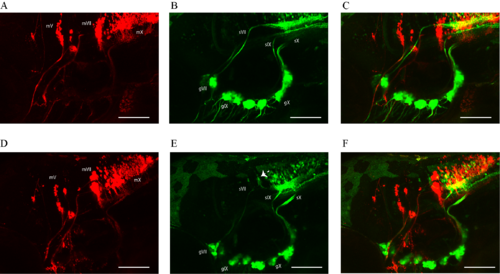
Crispr/Cas9 targeting of adam19b in Tg(3.2:egfp:hsp70:nsfB-mcherry.crest) larvae expressing mCherry in motor neurons and egfp in epibranchial sensory ganglia. Panels (A–C)represent control fish: (A) shows motor neurons and axons (mV, mVII and mX; red channel:hsp70:nsfB-mcherry.crest), (B) shows epibranchial sensory ganglia (green channel:3.2:egfp; sVII, sIX and sX are the projections of the facial (gVII), glossopharyngeal (gIX) and vagus (gX) ganglia, respectively) and (C) shows a composite of both images. Panels (D–F) represent Crispr/Cas9 targeting of adam19b. Panel (D) shows unaffected mV, mVII and mX motor neurons (red channel:hsp70:nsfB-mcherry.crest), (E) shows misrouted epibranchial ganglia projections (dotted white arrow; green channel:3.2:egfp) and (F) shows a composite of both images. All images are oriented anterior to the left and dorsal at top. Scale bars = 100 μm. |