- Title
-
EpCAM Is an Endoderm-Specific Wnt Derepressor that Licenses Hepatic Development
- Authors
- Lu, H., Ma, J., Yang, Y., Shi, W., and Luo, L.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Cell
|
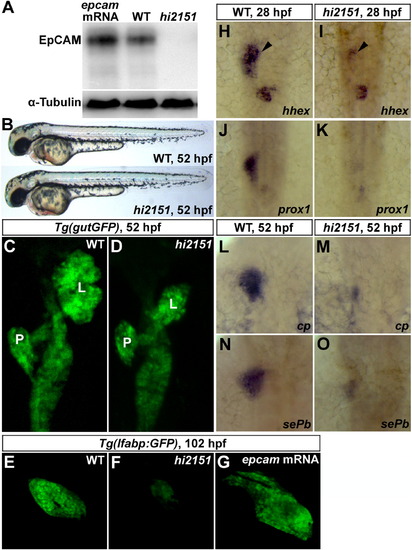
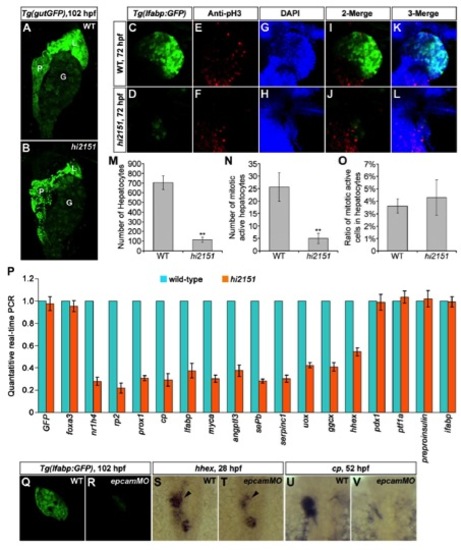
Liver Development Is Impaired in hi2151/epcam Zebrafish Mutant (A) Western blotting on the embryonic lysates at 24 hpf using antibodies against the ICD of zebrafish EpCAM. α-Tubulin serves as a loading control.(B) Except smaller otoliths, there is no obviously visible phenotype in hi2151 mutant embryos at 52 hpf.(C and D) Liver bud in hi2151 mutants (D, 41/60) is smaller than that in the wild-type (C, 55/56) at 52 hpf as observed under the Tg(gutGFP) transgenic background. L, liver; P, pancreas.(E–G) In contrast to the wild-type (E, 50/50), liver size is reduced in hi2151 mutants at 102 hpf (F, 52/72), whereas injection of epcam mRNA leads to enlarged liver (G, 45/59) as shown under the Tg(lfabp:GFP) transgenic background.(H–O) Expressions of hepatoblast specification markers hhex (H, 32/35; and I, 29/40; arrowheads) and prox1 (J, 36/37) (K, 28/37) at 28 hpf as well as differentiation markers cp (L, 39/41) (M, 27/39) and sePb (N, 31/34) (O, 30/38) at 52 hpf.See also Figures S1, S2, S6, and Table S1. |
|
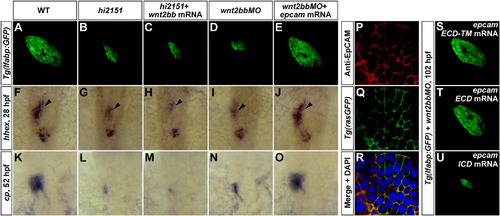
EpCAM Acts Downstream of Wnt2bb in Liver Development through Its Extracellular Domain(A–E) At 102 hpf, liver phenotypes in hi2151 mutants (B, 37/50) can not be rescued by wnt2bb mRNA (C, 33/46), whereas reduced liver size in wnt2bb morphants (D, 66/90) is rescued by epcam mRNA (E, 73/99) as shown under the Tg(lfabp:GFP) background.(F–O) Expressions of hhex (F–J, arrowheads) at 28 hpf and cp (K–O) at 52 hpf in the hepatic endoderm.(P–R) Antibody stainings illustrate the membrane enrichment of EpCAM on hepatocytes at 52 hpf (P), which is extensively colocalized with the membrane GFP signal under the Tg(rasGFP) background (Q and R).(S–U) Defective liver development in wnt2bb morphants at 102 hpf (D, 66/90) is rescued by either epcam ECD-TM (S, 51/66) or epcam ECD (T, 51/75) mRNA, but not rescued by epcam ICD mRNA (U, 72/78).See also Figures S1, S3, and Table S1. |
|
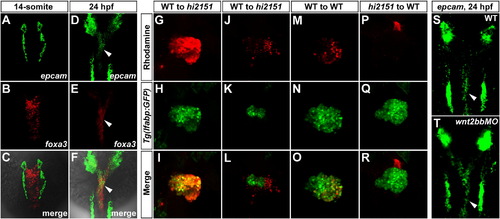
EpCAM Is Enriched in the Endoderm and Cell Autonomously Modulates Wnt2bb-Induced Hepatic Development(A–F) Double fluorescent in situ hybridizations (FISH) of epcam and foxa3 at the 14-somite stage (A–C) and 24 hpf (D–F). In the endoderm, note that epcam is not detected at the 14-somite stage, but enriched at 24 hpf (arrowheads). foxa3 is an endodermal marker.(G–R) Mosaic analyses using embryos injected with rhodamine-dextran as donors. Only wild-type donor cells massively contributing to the hepatic endoderm (G–I, n = 5), but not those contributing to the surrounding LPM (J–L, n = 8), are able to rescue the reduced liver size in hi2151 mutant acceptors. Transplanted wild-type donor cells (M–O, n = 8), but not hi2151 mutant donor cells (P–R, n = 10), are able to obviously contribute to the liver of wild-type acceptors. Tg(lfabp:GFP) transgenic background is applied in all the donors and acceptors. Transplanted embryos are imaged at 60 hpf.(S and T) As shown by FISH, expression of epcam in the endoderm at 24 hpf (S, 51/51, arrowhead) remains in wnt2bb morphants (T, 48/48, arrowhead).See also Figure S4 and Table S1. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
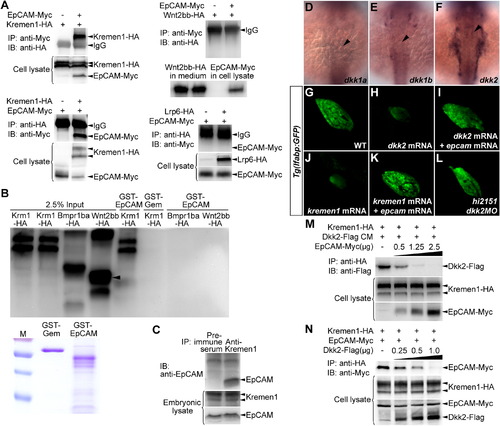
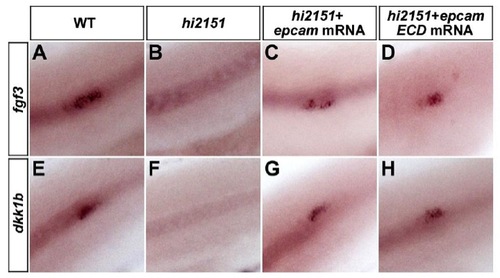
EpCAM Directly Binds to Kremen1 and Disrupts the Kremen1-Dkk2 Interaction(A) EpCAM-Myc and Kremen1-HA mutually coimmunoprecipitated from HEK293T cells, negatively controlled by Wnt2bb-HA and Lrp6-HA. IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblotting.(B) Kremen1-HA expressed in HEK293T cells is specifically pulled down by a GST-EpCAM fusion protein, but not by GST fused to an irrelevant nuclear protein Geminin (GST-Gem). Bmpr1ba-HA and Wnt2bb-HA expressed in HEK293T cells are applied as negative controls. Quantities of GST-Gem and GST-EpCAM recombinant proteins used in the pull-down assays were exhibited.(C) Controlled by preimmune serum, endogenous EpCAM in the embryonic lysate at 24 hpf coimmunoprecipitates with antibodies against Kremen1.(D–F) Expressions of dkk1a (D, 24/25), dkk1b (E, 26/29), and dkk2 (F, 12/15) at 24 hpf. Note that only dkk2 is present in the bilateral LPM domains adjacent to the hepatic endoderm (arrowheads).(G–L) Under the Tg(lfabp:GFP) background at 102 hpf, defects in liver development caused by dkk2 mRNA (H, 44/73) or kremen1 mRNA (J, 47/87) are rescued by epcam mRNA (I, 53/64) and (K, 99/135). Reduced liver size in hi2151 mutants is rescued by dkk2MO (L, 50/76).(M) In HEK293T cells, along with increases in the amount of epcam-Myc plasmid used for transfection (μg), the levels of coimmunoprecipitated Dkk2-Flag with Kremen1-HA get reduced.(N) In HEK293T cells, along with increases in the amount of dkk2-Flag plasmid used for transfection (μg), the levels of coimmunoprecipitated EpCAM-Myc with Kremen1-HA get reduced.See also Figures S1, S5, and Table S1. |
|
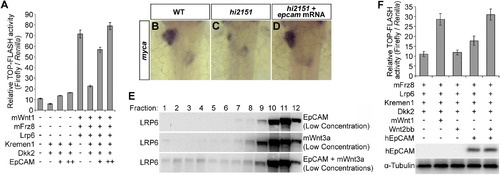
EpCAM Derepresses Wnt Targets and Cooperatively Activates Wnt Signaling with Wnt Ligand(A) TOP-FLASH firefly luciferase reporter assays normalized by Renilla luciferase activities. TOP-FLASH, Tcf-β-catenin reporter; m, mouse. Error bars represent SD.(B–D) In contrast to the wild-type control (B, 33/35), expression of myca in the liver-forming area is reduced in hi2151 mutants (C, 23/30), which is rescued by epcam mRNA (D, 29/36).(E) EpCAM and Wnt3a at low concentrations cooperatively allow formation of LRP6-signalosomes. The quantities of plasmids used for transfections are 10% of those used in Figure 5C.(F) TOP-FLASH luciferase reporter assays. HEK293T is an EpCAM deficient cell line. Note that Wnt2bb and EpCAM can cooperatively activate the reporter. h, human. Error bars represent SD.See also Table S1. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
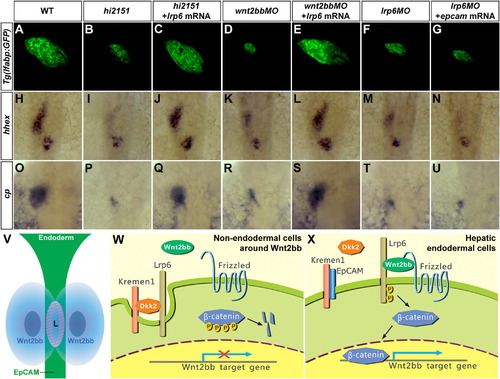
Lrp6 Is Required to Mediate the Roles of EpCAM and Wnt2bb in Hepatic Development(A–G) At 102 hpf, liver phenotypes in hi2151 mutants (B, 61/84) or wnt2bb morphants (D, 90/104) are rescued by lrp6 mRNA (C, 70/103; and E, 26/38), whereas reduced liver size in lrp6 morphants (F, 101/137) cannot be rescued by epcam mRNA (G, 78/102) as shown under the Tg(lfabp:GFP) background.(H–U) Expressions of hhex (H–N) at 28 hpf and cp (O–U) at 52 hpf in the hepatic endoderm.(V) A model of determinations of cell type and position of hepatic development. Presence of EpCAM in the endoderm and Wnt2bb at a specific anterior-posterior position in the LPM determine the cell type and the position of liver, respectively. They cooperatively activate Wnt2bb signaling in the hepatic endoderm. L, hepatic endoderm.(W) In nonendodermal cells around Wnt2bb, EpCAM is absent. Lrp6 forms an inhibitory ternary complex with Kremen1 and Dkk2. Thus, Lrp6 is removed from the cell surface and Wnt2bb signaling is not licensed.(X) In hepatic endodermal cells, EpCAM directly binds to Kremen1, which disrupts the Dkk2-Kremen1 interaction. This stabilizes Lrp6 on the endodermal cell surface and allows formation of active Lrp6-signalosomes, licenses, and cooperatively activates Wnt2bb signaling for hepatic development.See also Figures S1, S7, and Table S1. |
|
Defective Liver Development in hi2151 Mutants or epcam Morphants. related to Figure 1 EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
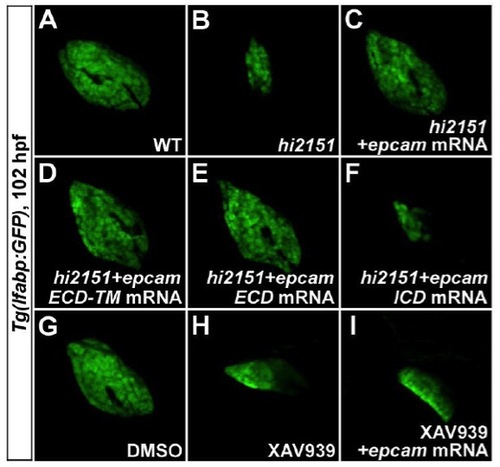
Rescue of hi2151 Mutant or XAV939 Treatment Phenotypes by EpCAM or Its Subdomains. related to Figure 2 |
|
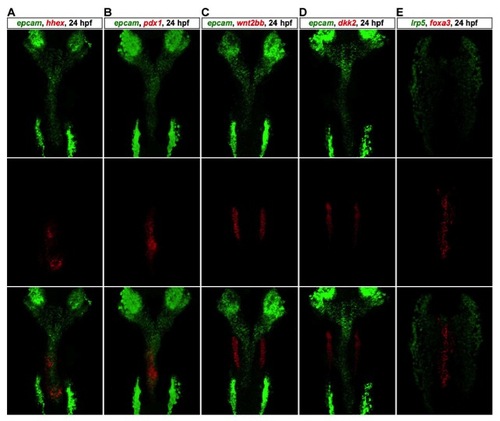
Double Fluorescent In Situ Hybridizations (FISH). related to Figure 3 Double FISH analyses of epcam and hhex (A), epcam and pdx1 (B), epcam and wnt2bb (C), epcam and dkk2 (D), lrp5 and foxa3 (E) at 24 hpf. Note that wnt2bb and dkk2 express in the bilateral LPM domains neighboring the hepatic endoderm, and lrp5 is absent in the endoderm. |
|
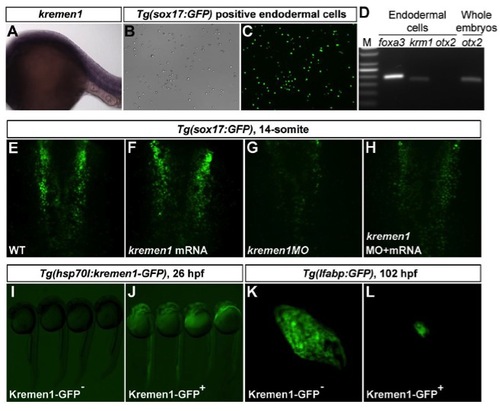
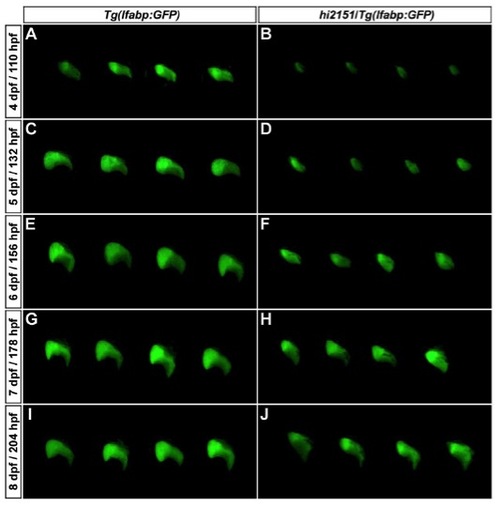
kremen1 Is Present in the Endoderm at 24 hpf, and Its Roles in Early Endoderm and Liver Development. related to Figure 4 EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Liver Regeneration Is Effective in hi2151 Mutant Embryos. related to Figure 1 |
|
Extracellular Domain of EpCAM Is Active to Modulate Wnt Signaling in Lateral Line Primordia. related to Figure 7 |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 24(5), Lu, H., Ma, J., Yang, Y., Shi, W., and Luo, L., EpCAM Is an Endoderm-Specific Wnt Derepressor that Licenses Hepatic Development, 543-553, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell