- Title
-
Celf1 regulation of dmrt2a is required for somite symmetry and left-right patterning during zebrafish development
- Authors
- Matsui, T., Sasaki, A., Akazawa, N., Otani, H., and Bessho, Y.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
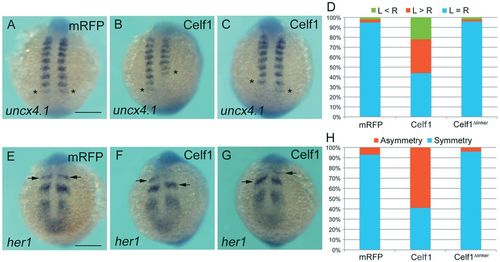
Overexpression of celf1 leads to defects in bilateral symmetry of the somites. (A-C) Representative images of uncx4.1 expression demonstrating symmetric (mRFP; A), left-biased (Celf1; B) or right-biased (Celf1; C) asymmetric somitogenesis in zebrafish embryos at 12-14 hpf. Dorsal view, anterior to the top. Asterisks mark the last-formed somite. (D) Percentages of symmetric (L=R), left-biased (L>R) or right-biased (L<R) asymmetric somitogenesis in mRFP- (n=60), celf1-(n=89) or celf1Δlinker- (n=60) overexpressing embryos. (E-G) Representative images of her1 expression demonstrating symmetric (mRFP; E) or asymmetric (Celf1; F,G) oscillation in embryos at 12-14 hpf. Arrows indicate the position of the anterior strip of her1. Vegetal pole view. (H) Percentages of symmetric and asymmetric her1 oscillation in mRFP- (n=87), celf1-(n=98) or celf1Δlinker- (n=76) overexpressing embryos. Scale bars: 200 μm. |
|
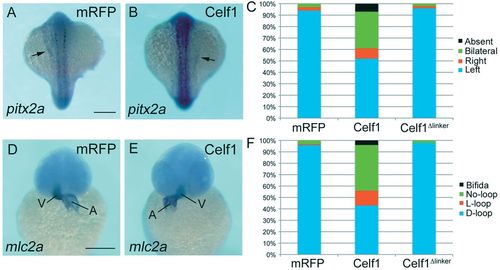
Overexpression of celf1 results in failures of LR asymmetric patterning. (A,B) Representative images showing left- (mRFP; A) or right- (Celf1; B) sided expression of pitx2a in zebrafish embryos at 18-19 hpf. Dorsal view, anterior to the top. Arrows indicate pitx2a expression in the lateral plate mesoderm. (C) Percentages of left-sided, right-sided, bilateral, or no (absent) expression of pitx2a in mRFP- (n=92), celf1-(n=102) or celf1Δlinker- (n=55) overexpressing embryos. (D,E) Representative images of mlc2a expression showing D-loop (mRFP; D) or L-loop (Celf1; E) of the heart in embryos at 42-45 hpf. Ventral view, anterior to the top. A, atrium; V, ventricle. (F) Percentages of D-loop, L-loop, no-loop or cardia bifida of the heart in mRFP- (n=92), celf1-(n=102) or celf1Δlinker- (n=51) overexpressing embryos. Scale bars: 200 μm. |
|
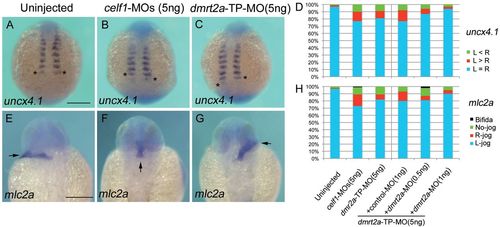
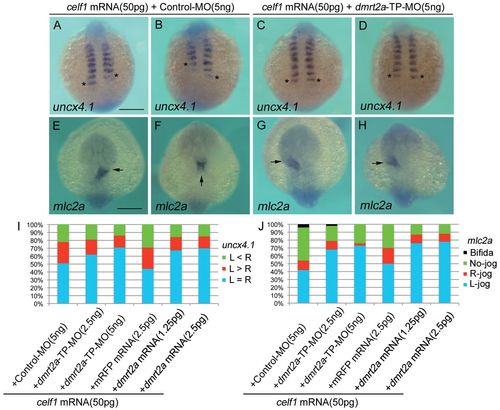
Knockdown of celf1 leads to defects in somite symmetry and LR patterning. (A-C) Representative images of uncx4.1 expression demonstrating symmetric (uninjected; A), right-biased (celf1-MOs; B) or left-biased (dmrt2a-TP-MO; C) asymmetric somitogenesis in zebrafish embryos at 12-14 hpf. Dorsal view, anterior to the top. Asterisks mark the last-formed somite. (D) Percentages of symmetric (L=R), left-biased (L>R) or right-biased (L<R) asymmetric somitogenesis in embryos injected with 5 ng control-MO (n=121), 5 ng celf1-MOs (n=102), 5 ng dmrt2a-TP-MO (n=90), 5 ng dmrt2a-TP-MO plus 1 ng control-MO (n=40), 5 ng dmrt2a-TP-MO plus 0.5 ng dmrt2a-MO (n=60) or 5 ng dmrt2a-TP-MO plus 1 ng dmrt2a-MO (n=68). (E-G) Representative images of mlc2a expression showing L-jog (uninjected; E), no-jog (celf1-MOs; F) or R-jog (dmrt2a-TP-MO; G) of the heart in embryos at 24-28 hpf. Dorsal view, anterior to the top. Arrows indicate the direction of heart jogging. (H) Percentages of L-jog, R-jog, no-jog or cardia bifida of the heart in embryos injected with 5 ng control-MO (n=152), 5 ng celf1-MOs (n=90), 5 ng dmrt2a-TP-MO (n=76), 5 ng dmrt2a-TP-MO plus 1 ng control-MO (n=46), 5 ng dmrt2a-TP-MO plus 0.5 ng dmrt2a-MO (n=47) or 5 ng dmrt2a-TP-MO plus 1 ng dmrt2a-MO (n=46). Scale bars: 200 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
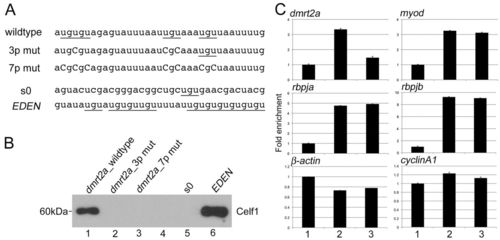
Celf1 binds to dmrt2a mRNA in vitro and in vivo. (A) Sequences of RNA oligonucleotide probes used in vitro binding assay. Underlines mark UGU repeats and capital letters indicate substituted nucleotides. (B) Binding of Celf1 with specific RNA was tested by in vitro binding assay. Lane 1: dmrt2a_wildtype; lane2: dmrt2a_3p mut; lane 3: dmrt2a_7p mut; lane 4: empty; lane 5: s0 (negative control); lane 6: EDEN (positive control). Interaction between Celf1 and either dmrt2a_wildtype (lane 1) or EDEN (lane 6) was detected. (C) In vivo interaction between Celf1 with dmrt2a (upper left panel), myod (upper right panel), rbpja (middle left panel), rbpja (middle right panel), β-actin (lower left panel) or cyclinA1 (lower right panel) mRNAs. Column 1: RIP control sample using normal serum from uninjected embryos; column 2: RIP sample using Celf1 antiserum (Celf1 AS) from uninjected embryos; column 3: RIP sample using Celf1 AS from embryos injected with dmrt2a-TP-MO. Celf1 interacted with dmrt2a, myod, rbpja and rbpjb mRNAs. dmrt2a-TP-MO specifically blocked the interaction of Celf1 with dmrt2a mRNA. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Celf1 promotes dmrt2a mRNA decay in vivo. (A) Effect of Celf1 on dmrt2a expression in zebrafish embryos. Total RNAs extracted from embryos injected with control-MO, celf1-MOs, dmrt2a-TP-MO, mRFP mRNA, celf1 mRNA or celf1Δlinker mRNA at 12-14 hpf were subjected to qPCR for dmrt2a and β-actin. The samples were normalized to β-actin as a reference. (B) dmrt2a mRNA is stabilized in embryos injected with celf1-MOs or dmrt2a-TP-MO. Decay rate of dmrt2a mRNA was assessed in embryos injected with control-MO, celf1-MOs or dmrt2a-TP-MO by qPCR following transcription inhibition using Actinomycin D. The samples were normalized to β-actin as a reference. control-MO: t1/2=317±11 minutes; celf1-MOs: t1/2=835±3 minutes; dmrt2a-TP-MO: t1/2=1487±4 minutes. Error bars represent s.d. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Disruption of Celf1-dmrt2a mRNA interaction cancels the effects of celf1 overexpression on somite symmetry and LR asymmetric patterning. (A-D) Representative images of uncx4.1 expression showing left-biased (celf1 mRNA plus control-MO; A), right-biased (celf1 mRNA plus control-MO; B) or symmetric (celf1 mRNA plus dmrt2a-TP-MO; C,D) somitogenesis in zebrafish embryos at 12-14 hpf. Dorsal view, anterior to the top. Asterisks mark the last-formed somite. (E-H) Representative images of mlc2a expression showing R-jog (celf1 mRNA plus control-MO; E), no-jog (celf1 mRNA plus control-MO; F) or L-jog (celf1 mRNA plus dmrt2a-TP-MO; G,H) of the heart in embryos at 24-28 hpf. Dorsal view, anterior to the top. Arrows indicate the direction of heart jogging. (I) Percentages of symmetric (L=R), left-biased (L>R) or right-biased (L<R) asymmetric somitogenesis in embryos injected with 50 pg celf1 mRNA and either 5 ng control-MO (n=70), 2.5 ng dmrt2a-TP-MO (n=43), 5 ng dmrt2a-TP-MO (n=79), 2.5 pg mRFP mRNA (n=55), 1.25 pg dmrt2a mRNA (n=69) or 2.5 pg dmrt2a mRNA (n=70) which lacks Celf1-binding site. (J) Percentages of L-jog, R-jog, no-jog, or cardia bifida of the heart in embryos injected with 50 pg celf1 mRNA and either 5 ng control-MO (n=98), 2.5 ng dmrt2a-TP-MO (n=62), 5 ng dmrt2a-TP-MO (n=92), 2.5 pg mRFP mRNA (n=56), 1.25 pg dmrt2a mRNA (n=55) or 2.5 pg dmrt2a mRNA (n=62), which lacks Celf1-binding site. Scale bars: 200 μm. |
|
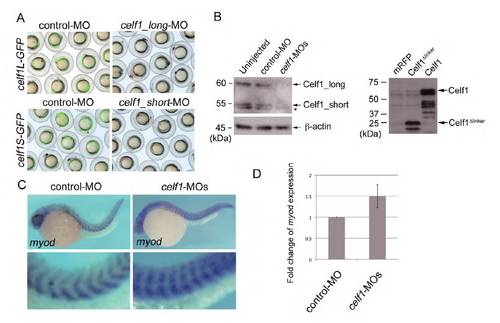
celf1 plays a crucial role in symmetric somitogenesis and LR asymmetric patterning. (A) celf1_long-MO and celf1_short-MO inhibited the expression of celf1L-GFP and celf1S-GFP, respectively. (B) Western blotting using anti-Celf1 antiserum. Left panel: co-injection of celf1_long-MO with celf1_short-MO (celf1-MOs) inhibited the expression of both forms of endogenous Celf1 in zebrafish embryos. The asterisk indicates a non-specific band. Right panel: Celf1 and Celf1Δlinker proteins were detected in Celf1- and Celf1Δlinker_overexpressing embryos, respectively. (C) Representative images of myod expression demonstrating normal (left; control-MO, n=105) or abnormal (right; celf1-MOs, n=88) somitogenesis in embryos at 24-28 hpf. Higher magnification images (lower panels) highlight somites. Knockdown of celf1 resulted in a mild loss of the chevron shape of somites (94%). (D) Upregulation of myod expression in celf1 morphants. qPCR assay revealed that celf1 knockdown resulted in a 50% increase of myod expression in zebrafish embryos, suggesting that myod is a target of Celf1 not only in C2C12 (Lee et al., 2010) but also in zebrafish. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
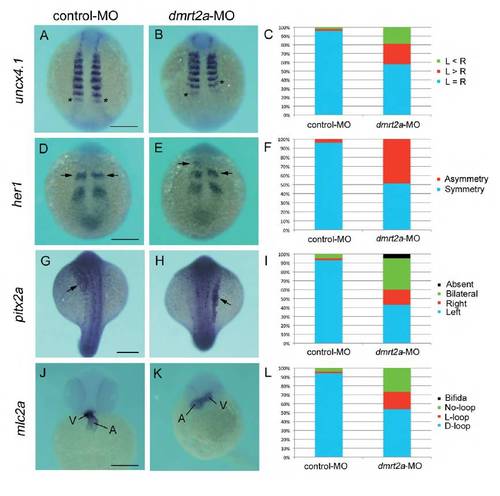
Knockdown of dmrt2a yields defects similar to those seen in celf1-overexpressing embryos. (A,B,D,E,G,H,J,K) In situ hybridization for uncx4.1 (A,B), her1 (D,E), pitx2a (G,H) or mlc2a (J,K) in control- MO-injected (A,D,G,J) or dmrt2a-MO-injected (B,E,H,K) embryos. Asterisks in A and B mark the last-formed somite. Arrows in D, F, G and H indicate the position of the anterior strip of her1 and pitx2a expression in the lateral plate mesoderm, respectively. A, atrium; V, ventricle. Scale bar: 200 μm. (C) Percentages of symmetric (L=R), left-biased (L>R) or right-biased (L<R) asymmetric somitogenesis in embryos injected with control- MO (n=44) or dmrt2a-MO (n=53). (F) Percentages of symmetric and asymmetric her1 oscillation in embryos injected with control-MO (n=48) or dmrt2a-MO (n=51). (I) Percentages of left-sided, right-sided, bilateral, or no (absent) expression of pitx2a in embryos injected with control-MO (n=59) or dmrt2a-MO (n=46). (L) Percentages of D-loop, L-loop, no-loop or cardia bifida of the heart in embryos injected with control-MO (n=58) or dmrt2a-MO (n=78). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
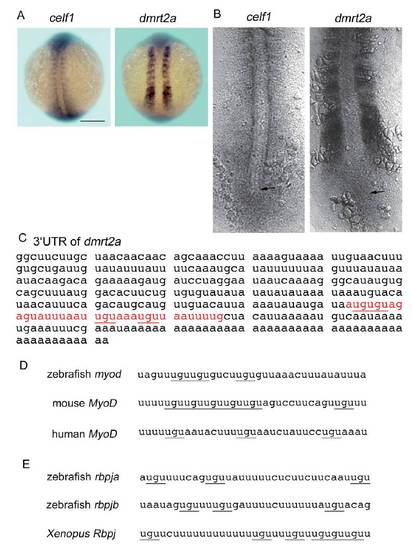
dmrt2a mRNA is a target of Celf1. (A,B) celf1 (left) or dmrt2a (right) expression in zebrafish embryos at 12-14 hpf. (A) Dorsal view of whole-mount embryos. Scale bar: 200 μm. (B) Dorsal view of flatmounted embryos. Arrows mark the position of Kupffer’s vesicle. (C) Sequence of the 3UTR of dmrt2a mRNA. Red letters are the putative Celf1-binding site including UGU repeats (underlined), and U- and A-rich sequences. The 35 nucleotides were used as a probe named dmrt2a_wildtype for an in vitro binding assay (see also Fig. 4A). (D,E) The putative Celf1-binding sites including UGU repeats (underlined) and U- and A-rich sequences were found within 3UTR of myod (D) or rbpj (E) mRNA, but sequence homology was low among species. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
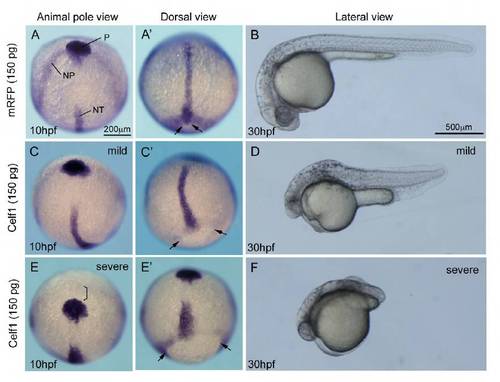
Higher amounts of celf1 mRNA lead to additional defects in zebrafish. (A,C,E) Expression of hgg1 (P, polster), dlx3 (NP, anterior edge of the neural plate) or ntl (NT, notochord) in embryos injected with mRFP (A) or celf1 (C,E) mRNAs (150 pg). Animal pole view. Scale bar: 200 μm. (A′,C′,E′) Dorsal view of the embryo, anterior to the top. Injection of 150 pg celf1 mRNA resulted in the formation of bended (C) or short (E′) notochord. The polster did not reach the anterior edge of the neural plate (bracket in E). Epiboly was incomplete (C′,E′). Arrows in A′, C′ and E′ mark edge of the yolk plug. (B,D,F) Lateral view of embryos injected with mRFP (B) or celf1 (D, F) mRNAs (150 pg) at 30 hpf. Various phenotypes, such as short tails, segmentation defects, small eyes, small heads and less pigmentation, were observed (D,F). |