- Title
-
Cep70 and Cep131 contribute to ciliogenesis in zebrafish embryos
- Authors
- Wilkinson, C.J., Carl, M., and Harris, W.A.
- Source
- Full text @ BMC Cell Biol.
|
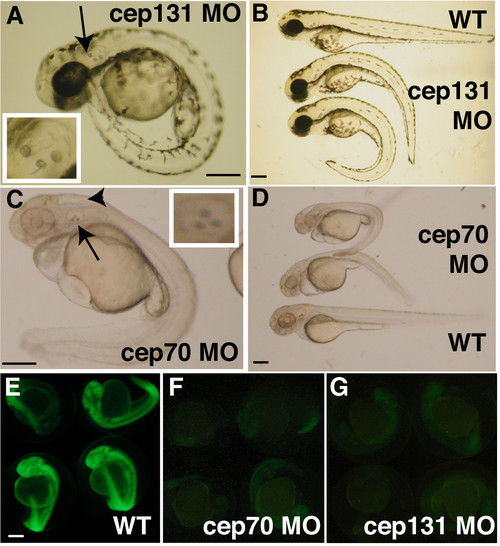
cep70 and cep131 morphants at 48 h.p.f. cep131 (A, B) and cep70 (C, D) with WT embryos shown at the top (B) and bottom (D) with morphants of varying severity as judged by curvature of the spine. The ectopic third otolith can be easily seen in (A) and (C), is labelled with an arrow and the otic vesicle is magnified in the insets. There is an arrowhead to the hydrocephaly present in the cep70 morphant in (C). To demonstrate morpholino effectiveness, embryos were co-injected with morpholino and an mRNA encoding the morpholino target site spliced in frame to GFP. In these embryos (F, G), expression was greatly reduced compared to embryos not injected with morpholino to another target sequence (E). Very little signal – much of it autofluorescence – could be detected when exposure time was increased to 8″ for morphants (F, G) compared to 1/8″ for control (E); otherwise panels would be blank. cep70 morphants and corresponding control embryos were treated with PTU hence the lack of pigmentation. Scale bar: 250 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
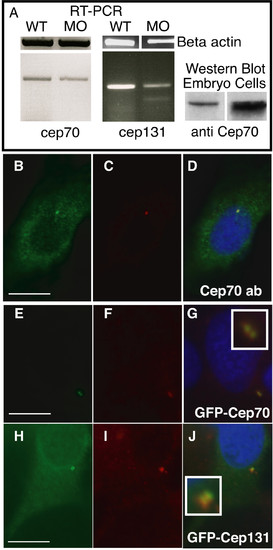
Subcellular localisation of Cep70 and Cep131. (A) Splicing-inhibitory morpholinos result in a reduction in cep70 and cep131 mRNA levels, as judged by RT-PCR of a 480 bp or a 360 bp fragment, respectively, that covers the splice site. In the cep131 morphant, an additional, faint band at 260 bp can be observed. This is consistent with skipping of the third exon, though other splicing products might also be possible. Right, an antibody to Cep70 recognises a 70 kDa band in PC2 cell line and zebrafish embryo extract. (B-J) Subcellular localisation of Cep70 and Cep131. An antibody raised to Cep70 gives a punctate staining (B) similar to gamma tubulin (C) in PC2 zebrafish cultured fibroblasts. The two signals coincide when the two channels are merged, the centrosome now shown in yellow (D). GFP-Cep70 and GFP-Cep131 localise to the centrosome, as expected (E-J). Cep70 or GFP fusions are shown in green, gamma tubulin is in red, nuclei are in blue (DAPI) in merged pictures. Insets enlarge the centrosome signal. Scale bar: 10 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
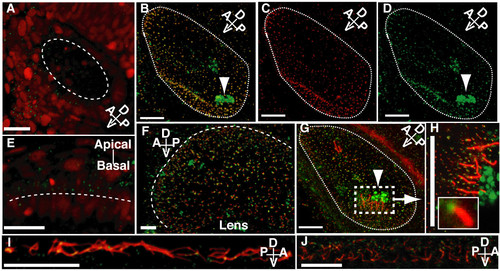
Confocal wholemount (immuno)fluorescence localisation of Cep70 in zebrafish embryos. (A and E) In embryos injected with GFP-Cep70 and H2B-RFP, the Cep70 signal, though weak, is observed at the apical surface of cells in the otic vesicle (A) and eye (E) at 24 h.p.f. . Long dashed lines indicate the apical surface: interior to the circle in (A) and above the line in (E). Other panels: 24 h.p.f. zebrafish embryos were probed with anti-Cep70 (green) and either anti-acetylated or anti-gamma tubulin (red). (B, C, D) Otic vesicle stained for gamma tubulin (C), Cep70 (D) and merged picture (B) showing that the two signals coincide. Arrowheads point to the non-specific staining of the otoliths. (F) and (G) show the eye and otic vesicle; Cep70 can be seen at the base of cilia stained for acetylated-tubulin. (H) shows the region around one of the clusters of tether cells in the otic vesicle where the position of Cep70 can be seen more clearly; an inset shows one basal body and cilium. Yellow colour, the overlap of Cep70 and acetylated-tubulin signal is due to the angle at which some of the cilia are seen. Again, a long dashed line indicates the apical surface of the eye in (F). Short dashed lines delineate the otic vesicle in (B, C, D and G). (I) and (J) show Cep70 and cilia in the pronephros and spine canal. Again the Cep70 can be seen at the base of cilia. Orientation of the specimens with regard to the embryo is shown by the compass in the panel: A = anterior, P = posterior, D = dorsal, V = ventral. Scale bar: 20 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
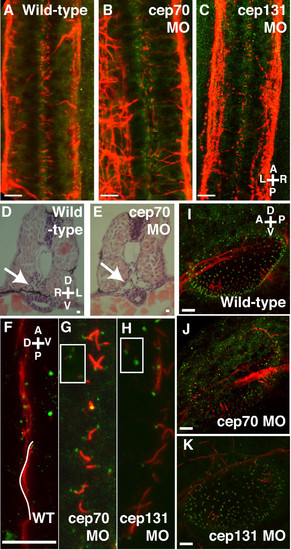
Cilia in the otic vesicle, spine and pronephros at 30 h.p.f. (A-C) Spine of WT, cep70 and cep131 morphants, stained for acetylated tubulin (red, cilia) and gamma tubulin (green, basal bodies). The cilia of the central canal can be seen in between the two nerve tracts. Cilia are shortened in the morphant embryos but basal bodies remain intact. Pronephric ducts – arrows – are enlarged in morphant cep70 embryos (E) compared to WT (D) at 48 h.p.f. . (F-H) Cilia are also reduced in length in the pronephros of the morphants (G, H) compared to WT (F). However, like other tissues, basal bodies are present. Basal bodies are also present in surrounding tissues (inset). One WT cilium has been colored white for clarity. (I-K) Otic vesicles of WT, cep70 and cep131 morphants. Compass in the panels shows orientation: A = anterior, P = posterior, D = dorsal, V = ventral, L = left, R = right. Scale bars: 10 μm. |
|
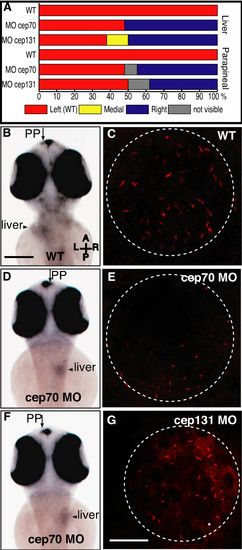
Asymmetry in cep70 and cep131 morphants. (A) Randomisation of asymmetry of liver and parapineal in cep70 (n = 27) cep131 (n = 16) compared to WT (n = 21) where both are on the left hand side. (B, D, F) Position of asymmetrically placed organs in cep70 morphants compared to WT, at 60 h.p.f., assayed by wholemount in situ hybridisation for otx5 and fkd2 which label the parapineal (PP) and liver. In WT (B), both are placed on the left hand side. In cep70 morphants, this is randomised but not concordantly: the embryo in (D) has the position of both liver and parapineal inverted whereas the embryo in (F) has them on opposite sides – liver inverted, parapineal normal. Scale bar: 250 μm. Compass shows embryo orientation in which A = anterior, P = posterior, L = left and R = right. (C, E and G) Cilia in Kupffer's vesicle in WT, cep70 and cep131 morphants. Cilia are much shorter in the morphant embryos. Dashed circle outlines the vesicle. Scale bar: 20 μm. |
|
Convergence-extension is unaffected in cep70 morphants. (A-F) Defective epiboly in cep70 morphant (cep131 morphants normal at this stage). At 70% epiboly, morphant embryos (B) have an acorn shape, unlike normal development at this stage (A). As epiboly completes, morphant embryos (D) (WT shown in C) extrude some of the yolk but will recover and survive. Assaying convergence-extension by the distance between anterior neural margin and prechordal plate by wholemount in situ hybridisation for dlx3 (purple) and hgg1 (light blue) reveals no difference between morphant (F) and WT (E). Scale bar: 125 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Subcellular localisation of Cep70 and Cep131 fragments. The N-terminus of Cep70 localises to the centrosome (A) whereas the C-terminus does not (B). Both the N-terminus, IQ (blue square) and HDAC-ID (red hexagon) domains of Cep131 are required for centrosomal localisation (F). (I) depicts which fragments were fused to GFP and the panels in which they are represented. (G) and (H) show aggregates generated by overexpression GFP fusions of the N-terminal fragment and full-length Cep70. GFP fusions are shown in green, gamma tubulin is in red, nuclei are in blue (DAPI) in merged pictures. Scale bar: 10 μm. |
|
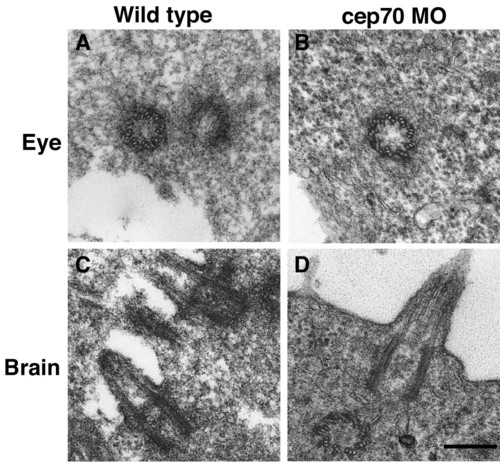
Micrographs of basal bodies and cilia from WT and cep70 morphant zebrafish embryos. An eye centriole and brain cilium from 24 h.p.f. WT (A, C) and morphant (B, D) are shown. Scale bar: 250 nm PHENOTYPE:
|