Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250925-7
- Publication
- Olaya et al., 2025 - Distinct cellular and reproductive consequences of meiotic chromosome synapsis defects in syce2 and sycp1 mutant zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
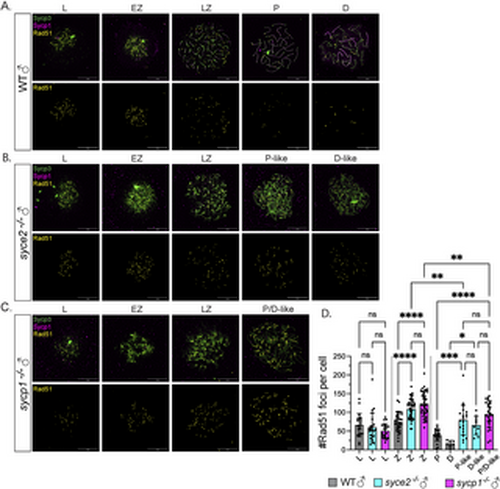
Inefficient DSB repair in syce2-/- and sycp1-/- mutants during prophase. (A–C) Surface-spread chromosomes from wild-type (A), syce2-/- (B) and sycp1-/- (C) spermatocytes immunostained for Sycp3 (green), Sycp1 (magenta) and Rad51 (yellow). Examples of spread chromosomes from meiotic prophase I: L, EZ, LZ, P, D, P-like (syce2-/-) and P/D-like(sycp1-/-). D-like nuclei (syce2-/-) are categorized as having full-length axes, but Sycp1 is largely absent from pseudo-synapsed regions throughout the nucleus. Scale bar = 10 µm. (D) Number of Rad51 foci per cell using data from (A–C). EZ to LZ nuclei are grouped together as zygotene (Z). Data is pooled from 2 independent experiments. n = 21, WT – L; n = 23, syce2-/- – L; n = 22, sycp1-/- – L; n = 34, WT – Z; n = 41, syce2-/- – Z; n = 44, sycp1-/- – Z; n = 22, WT – P; n = 7, WT – D; n = 21, syce2-/- – P-like; n = 10, syce2-/- – D-like; n = 26, sycp1-/- – P/D-like. Significance was determined using ordinary one-way ANOVA testing with Šidák’s multiple comparisons test. ns = not significant; ** = p < 0.01; *** = p < 0.001; **** = p < 0.0001. |