Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250814-51
- Publication
- Kelu et al., 2025 - Muscle peripheral circadian clock drives nocturnal protein degradation via raised Ror/Rev-erb balance and prevents premature sarcopenia
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
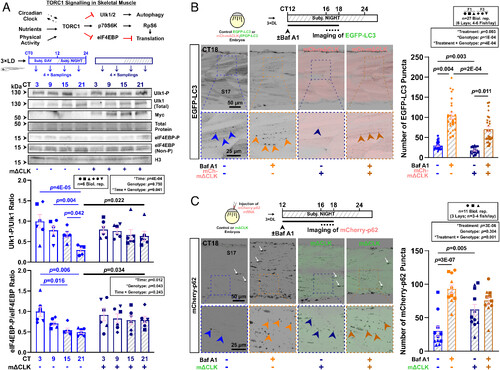
Inhibition of the muscle clock reduces autophagosome formation and autophagic activity in muscle at night. (A) The TORC1 signaling pathway in skeletal muscle highlighting relevant downstream effectors. Effect of muscle clock inhibition on circadian oscillation of Ulk1Ser757 and eIF4EBPThr37/46 phosphorylation in entrained larvae under free-run between 3 and 4 dpf in control and mΔCLK siblings. Statistics are two-way ANOVA (Time/Genotype) with Bonferroni’s post hoc test. (B) Autophagic flux in muscle measured in Tg(CMV:EGFP-map1lc3b)zf155 control and sibling Tg(CMV:EGFP-map1lc3b)zf155;mCherry-mΔCLKkg334Tg DL-entrained larvae under free-run between 3 and 4 dpf treated with DMSO or bafilomycin A1 (Baf A1) at CT12 for 4 to 6 h. Confocal parasagittal images at CT16-18 visualized the number of EGFP-LC3 puncta (arrowheads) in S17. Statistics are two-way ANOVA (Treatment/Genotype) with Bonferroni’s post hoc test. F1/F3, filial generation. (C) Autophagic flux in muscle measured with mCherry-p62 mRNA injection at one-cell stage into sibling control and EGFP-mΔCLKkg333Tg transgenic embryos, which were entrained and under free-run treated with DMSO or bafilomycin A1 (Baf A1) at CT12 for 4 to 6 h. Confocal parasagittal images at CT16-18 visualized the number of mCherry-p62 puncta (arrowheads) in sarcoplasm in S17. Some signals also associated with nuclei (white arrows), as previously reported (28, 29). Statistics are two-way ANOVA (Treatment/Genotype) with Bonferroni’s post hoc test. |