Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250814-50
- Publication
- Kelu et al., 2025 - Muscle peripheral circadian clock drives nocturnal protein degradation via raised Ror/Rev-erb balance and prevents premature sarcopenia
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
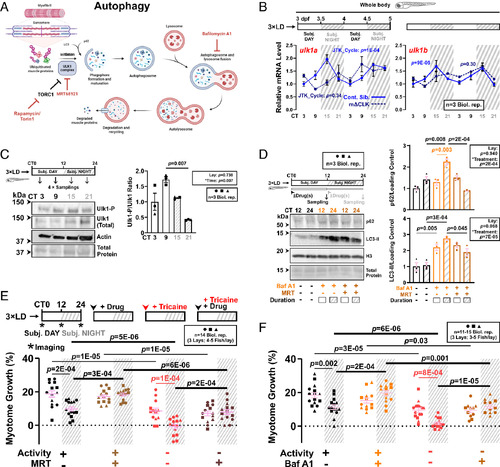
Ulk1-dependent autophagy activation at night limits nocturnal muscle growth. (A) The autophagy pathway highlighting relevant proteins and inhibitors (red). (B) Circadian mRNA levels of ulk1a and ulk1b in 3xLD entrained whole larvae of control and mΔCLK siblings under free-run analyzed by RT-qPCR (SI Appendix, Fig. S1C). Statistics from JTK_Cycle. (C) Circadian oscillation in Ulk1Ser757 phosphorylation in larvae under free-run between 3 and 4 dpf assessed by western blotting. Statistics are two-way ANOVA (Lay/Time) with Bonferroni’s post hoc test. (D) Circadian variations in autophagic degradation of p62 and LC3-II in larvae under free-run treated with DMSO, bafilomycin A1 (Baf A1) alone, or both Baf A1 and MRT68921 (MRT) during either CT0-12 or CT12-24 and analyzed by western blotting. Statistics are two-way ANOVA (Lay/Treatment) with Bonferroni’s post hoc test. (E and F) Circadian myotome growth after autophagy inhibition in entrained active or inactive larvae treated under free-run between 3 and 4 dpf with DMSO, MRT68921 (E), or bafilomycin A1 (F). Statistics are two-way ANOVA (Time/Treatment) with Bonferroni’s post hoc test. |