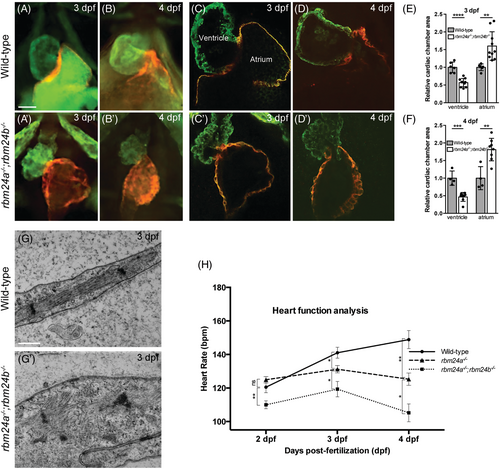
Disrupted integrity and function of cardiac muscles in rbm24a and rbm24b mutants. (A–D′) Immunofluorescence staining of ventricle and atrium in wild-type embryos and rbm24a−/−;rbm24b−/− double mutants. At each developmental stage, 15 to 20 embryos per genotype were analyzed. Scale bars: 5 μm. (E, F) Graphs measuring the ventricle and atrium size at 3 and 4 dpf, respectively. (G, G′) TEM images of heart sections. Wild-type embryos show highly organized sarcomeres with thin and thick myofilaments in well-aligned bundles and discernible dark A-band and light I-bands, while double mutant embryos display a complete disorganization of sarcomeric unit. At each developmental stage, 15 to 20 embryos per genotype were analyzed. Scale bars: 500 nm. (H) Graph comparing heart rate of rbm24a single mutants and rbm24a−/−;rbm24b−/− double mutants at 2, 3, and 4 dpf. Average heart rate with standard error was plotted and significant deviation was determined using the Student's t test. At each developmental stage, 15 to 20 embryos per genotype were analyzed.
|

