Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250526-29
- Publication
- Huang et al., 2025 - Agouti and BMP signaling drive a naturally occurring fate conversion of melanophores to leucophores in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
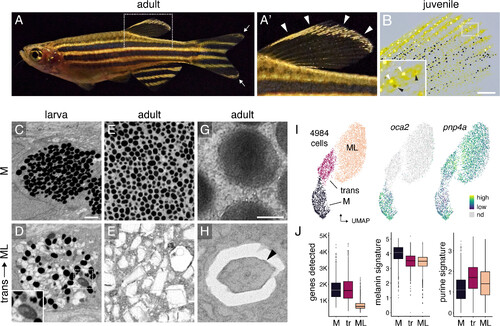
Melanoleucophore (ML) ornamentation and characteristics. (A and A′) ML occur along anterior and distal edges of the dorsal fin (arrowheads, A′) and in lesser numbers at the tips of the caudal fin (arrow, A). (B) Juvenile fish with white ML (white arrowheads, Inset) and gray transitional cells (black arrowheads). Pigmentary organelles have been contracted toward cell centers by epinephrine treatment; yellow pigments are contained within xanthophores. A second class of leucophore, xantholeucophores, occurs only in the anal fin (9) and these cells are not included in the present analyses. (C and D) In late larvae, melanophores (M) contain rounded melanosomes whereas transitional cells have heterogeneous pigmentary organelles including irregular or enlarged melanosomes (Inset). (E and F) In adults, melanophores contain rounded melanosomes whereas ML contain jagged leucosomes with crystalline contents. (G and H) Melanosome and leucosome with crystal (arrowhead). C–F, pigmentary organelles contracted to cell centers by epinephrine treatment, with imaging by focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy (FIB–SEM); G and H, transmission EM. (I) Single-cell transcriptomes in UMAP space with cell states (Left) and transcript abundances for melanogenesis gene oca2 and purine salvage gene pnp4a (Right). (J) Compared to melanophores, ML had fewer genes detected, fewer transcripts of genes for melanogenesis, and more transcripts of genes for purine synthesis. Boxplots, medians, and interquartile ranges. (Scale bars, B 200 µm, 8C for C–F 1 µm, G for G and H 0.2 µm.) |