Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250505-74
- Publication
- Yang et al., 2025 - The Serotonergic Dorsal Raphe Promotes Emergence from Propofol Anesthesia in Zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
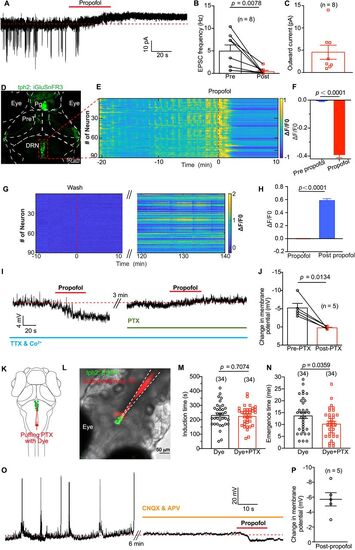
Propofol inhibits presynaptic excitatory glutamate inputs to DRN5-HT and cause membrane hyperpolarization of DRN5-HT. A, Spontaneous EPSCs of a DRN5-HT neuron (clamped at −60 mV) before and after puffing of propofol. The red dashed line indicates the mean leakage current before propofol application. B, Summary of data showing the reduction of EPSC frequency by propofol application. Pre versus post, 4.95 ± 1.36 Hz versus 0.40 ± 0.26 Hz; p = 0.001; paired Student's t test. N = 8 cells from different larvae. C, Summary of data showing the outward current induced by propofol application. N = 8 cells from different larvae. D, Transient expression of glutamate sensor by injecting UAS, iGluSnFR3 plasmid into Ki (tph2, GAL4FF; cmlc2, EGFP) line. Pg, pineal gland; PreT, pretectum; DRN, dorsal raphe nucleus. E, Representative heatmaps of glutamate events from DRN5-HT of one larva stimulated by dimming at 58 s interval. The red dash line indicates the timing of adding propofol to the dish. F, Glutamate events were significantly inhibited by 30 µM propofol. N = 259 DRN5-HT neurons from three larvae. G,H, iGlusnFR3 signal gradually recovered when propofol was washed by perfusion. I, Representative trace showing propofol-induced membrane potential changes of a DRN5-HT neuron before and after application of 100 mM PTX. During the recording, synaptic transmission was blocked by replacing Ca2+ with Co2+ in the extracellular solution and adding 1 mM TTX. J, Summary of data showing the effect of PTX on propofol-induced membrane potential changes. Without PTX versus with PTX, −5.2 ± 1.3 mV versus 0.2 ± 0.2 mV; n = 5; p = 0.013; paired Student's t test. K, Schematic diagram showing local puffing of PTX with the red fluorescent dye sulforhodamine 101. L, A typical case showing the area of puffing PTX with the red fluorescent dye sulforhodamine 101. M, N, Inhibiting GABAA receptors in DRN by local puffing PTX had no influence on induction time of propofol while significantly shortening the emergence time from propofol anesthesia (N, dye vs dye + PTX, 13.8 ± 1.2 min vs 10.3 ± 1.0 min; p = 0.036; unpaired Student's t test). O, P, After blocking glutamatergic receptors by adding 50 µM CNQX and 100 µM APV in the extracellular solution, local puffing of propofol caused a significant hyperpolarization of DRN5-HT (mean ± SEM, −5.7 ± 0.9 mV; n = 5 neuron). Numbers of the sample size are in parentheses. |