|
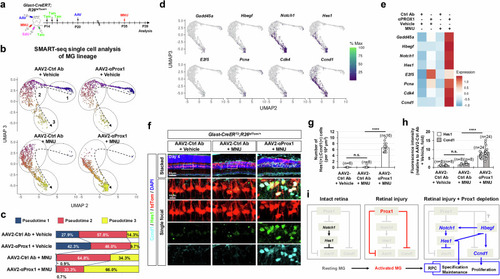
Injury-induced reprogramming of MG into RPCs upon reduced Prox1 transfer. a Retinas from Glast-CreERT;R26tdTom/+ mice infected with AAV2-Ctrl Ab or AAV2-αProx1 were injured using MNU. MG lineage cells were then purified by FACS at the indicated time points for SMART-seq analysis (a–e) or analyzed by immunostaining for RPC markers (f–h). b UMAP plots from Monocle 3 analysis of SMART-seq data for FACS-purified tdTom-positive cells in vehicle- or MNU-treated Glast-CreERT;R26tdTom/+ mouse retinas (details in Methods). Dotted arrows indicate pseudotime progression, with circled areas marking distinct populations by pseudotime intervals. c Pseudotime distributions of cell populations for each sample are shown. d Pseudotime distributions of cells expressing RPC and proliferative cell marker mRNAs are plotted. e Heatmap displaying the mean expression levels of the indicated mRNAs in each sample. f Distribution of Ccnd1 and Hes1 in AAV2-infected Glast-CreERT;R26tdTom/+ mouse retinas was assessed by immunostaining. Magnified views of boxed areas in the top row are shown in the subsequent rows. g, h Graphs show the number of Ccnd1 and Hes1 double-positive cells (g) and the relative intensity of Ccnd1 and Hes1 in these cells (h). Error bars denote SEM. ****, p < 0.001; n.s., > 0.05 (one-sided Student’s t-test). i A hypothetical model illustrating the negative regulation of injury-induced MG reprogramming into RPCs by Prox1.
|