Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250116-29
- Publication
- Lin et al., 2024 - Elucidating tobacco smoke-induced craniofacial deformities: Biomarker and MAPK signaling dysregulation unraveled by cross-species multi-omics analysis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
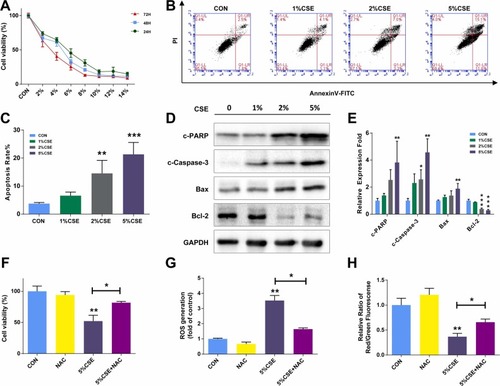
CSE Exposure Inhibits Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis via Reactive Oxygen Species Mediates in HEPM Cells. (A) CCK-8 assay results demonstrating the viability of HEPM cells exposed to different concentrations of CSE for 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h. (B, C) Flow cytometry analysis of apoptosis in HEPM cells exposed to 1 %, 2 %, and 5 % CSE for 24 h using Annexin V-FITC/PI double staining. (D, E) Western blot assays showing the expression of apoptosis-associated proteins (cleaved-PARP, cleaved-caspase-3, bax, bcl-2) in HEPM cells exposed to 1 %, 2 %, and 5 % CSE for 24 h. Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (GAPDH) served as a loading control. HEPM cells were treated with DMSO or NAC (reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenger), along with 5 % CSE exposure. (F) Cell viability detected by CCK-8 assay. (G, H) Bar charts showed ROS and mitochondrial membrane potential quantitative data by flow cytometry. Results are presented as mean ± SD. (n=3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). |