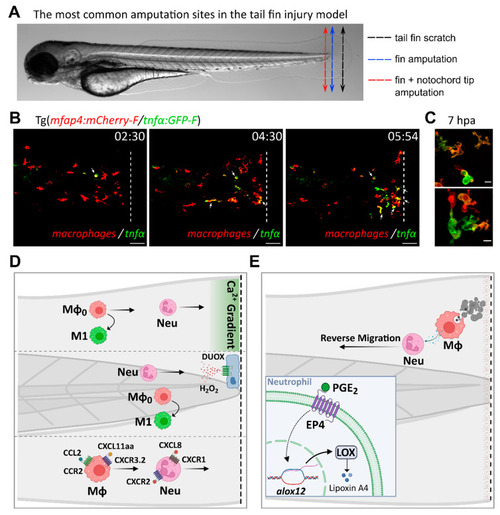
Inflammatory mediators and signaling pathways regulating leukocyte recruitment and activation during sterile injury, as inferred from the tail fin injury model. (A). The most common amputation/wounding sites used in the tail fin injury model are highlighted on a representative transmitted light image of a 3 dpf larva. Black dotted arrow: scratch on the tail fin tip. Blue dotted arrow: transection of the fin tip only, just before the notochord. Red dotted arrow: transection of the fin and the tip of the notochord. (B). Time-course of macrophage recruitment and activation following tail fin transection (intact notochord). Real-time imaging of the fin fold of a 3 dpf amputated larva from the Tg(mfap4:mCherry-F/tnfα:GFP-F) line, using confocal microscopy (unpublished data by Nguyen-Chi M. et al). In this line, macrophages and TNFα-expressing cells are labelled with red and green fluorescence, respectively. The representative frames show macrophage recruitment and activation toward an M1 phenotype at the wound, as previously observed by Sipka et al [53]. M1 macrophages, i.e., macrophages expressing TNFα, are indicated with white arrows. Time after amputation is indicated in hour:min. Dotted lines show the wound margin. Scale bar: 50 µm. (C). Representative images of activated macrophages at high magnification at 7 h post-amputation (unpublished data by Nguyen-Chi M. et al). Scale bar: 10 µm. (D). Tail wounding with fin amputation only. Upper part: fin wounding triggers instantaneous calcium flashes that are required for the recruitment of both neutrophils and macrophages. Ca2+ signaling is also important for macrophage polarization toward M1-like phenotype [53]. Middle part: reactive oxygen species H2O2 induces the recruitment of neutrophils at the wound site [112,113]. ROS are also required for macrophage M1-like activation [53]. Lower part: chemokines are essential for leukocyte recruitment to injury sites. Neutrophils migrate toward the wound via the CXCL8/CXCR1 axis while the CXCL8/CXCR2 axis promotes their dispersal [81,304]. By contrast, macrophage recruitment relies on CCL2/CCR2 and CXCL11aa/CXCR3.2 axes [221,225]. (E). Tail wounding with both fin and notochord tip amputation. Macrophage uptake of apoptotic cells triggers the resolution of inflammation by the production of PGE2 [285]. Mechanistically, PGE2 acts via EP4 receptors present on neutrophils, stimulating LOX expression. LOX activity then induces a lipid mediator switch that activates lipoxin production. Mϕ: macrophage. Neu: neutrophil.
|

