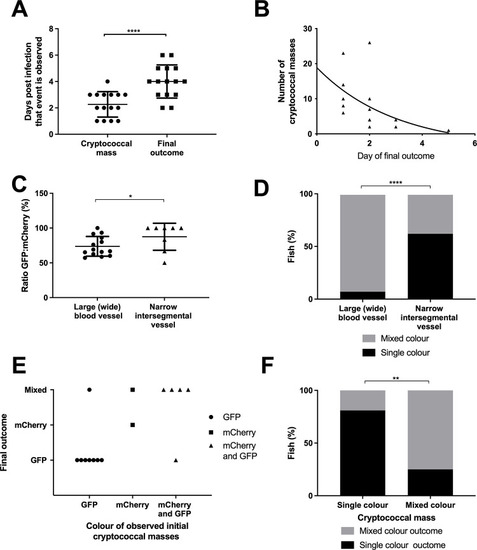
Fig 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-220426-29
- Publication
- Gibson et al., 2022 - Blood vessel occlusion by Cryptococcus neoformans is a mechanism for haemorrhagic dissemination of infection
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
Infection of 2 dpf AB larvae with 25 cfu of a 5:1 ratio of GFP:mCherry KN99 |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Condition: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | Long-pec to Day 4 |