Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-220327-9
- Publication
- Jawahar et al., 2022 - Starvation causes changes in the intestinal transcriptome and microbiome that are reversed upon refeeding
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
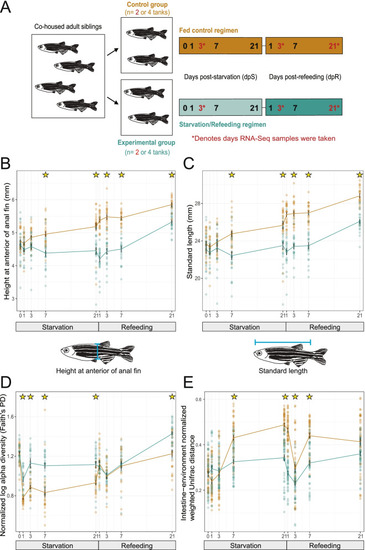
Starvation and refeeding affect zebrafish somatic growth as well as intestinal and environmental microbiome diversity. |