Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-220204-13
- Publication
- Hong et al., 2020 - In Situ Fucosylation of the Wnt Co-receptor LRP6 Increases Its Endocytosis and Reduces Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
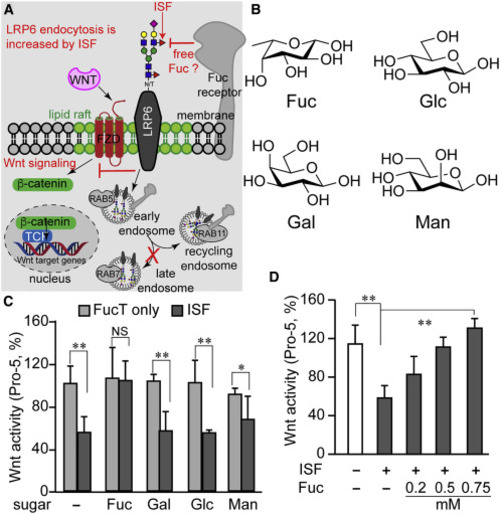
(A) Diagram summarizing our new findings and predicting the presence of a Fuc-binding receptor. Increasing cell-surface N-glycan LacNAc α(1–3)-fucosylation via ISF treatment exacerbates the endocytosis of the lipid-raft-localized Wnt receptor LRP6 which, in turn, leads to reduced Wnt/β-catenin signaling. The majority of endocytosed cell-surface LRP6 enters the recycling pathway rather than the degradation pathway following endocytosis induced by ISF treatment. (B) The chemical structure of four monosaccharides in a vertebrate N-glycan: L-fucose (Fuc), D-glucose (Glc), D-galactose (Gal), and D-mannose (Man). (C and D) Wnt-signaling activity in Pro-5 cells treated by ISF or FucT only, in the presence (C) or absence (D) of a free monosaccharide. Error bars represent SE of three biological replicates. Unpaired two-tailed Student's t test: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01; NS, not significant. |