Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-210217-25
- Publication
- Van Laar et al., 2020 - α-Synuclein amplifies cytoplasmic peroxide flux and oxidative stress provoked by mitochondrial inhibitors in CNS dopaminergic neurons in vivo
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
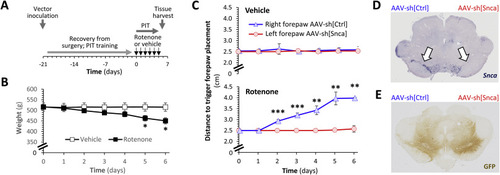
Fig. 1. α-Synuclein knockdown prevents rotenone-induced loss of dopaminergic function in vivo. A: Schematic depiction of the experimental sequence for the rat studies shown in panels B–E and in Fig. 2. B: Mean ± SE weight of rats treated with vehicle (white squares) or rotenone (2.8 mg/kg/day; black squares) by intraperitoneal injection over 6 consecutive days. p < *0.05 vehicle versus rotenone, 2-way repeated measures ANOVA with Šidák multiple comparisons test. C: Mean ± SE distance to trigger a corrective forelimb movement during postural instability tests in rats treated with vehicle (upper panel) or rotenone (lower panel). In each case, data are shown separately for the left forelimb (red; opposite to right hemisphere that received AAV-sh[Snca]) and right forelimb (blue; opposite the left hemisphere that received AAV-sh[Ctrl]). p < **0.01, **0.001, left vs. right, 2-way repeated measures ANOVA with Šidák multiple comparisons test. D, E: Micrographs showing midbrain sections from a vehicle-treated rat, labeled using (D) RNA in situ hybridization to detect the Snca mRNA transcript (purple) or (E) immunohistochemistry to detect expression of GFP (brown). Arrows in the upper panel indicate the substantia nigra. The side of the brain that received each vector is marked above the sections. |