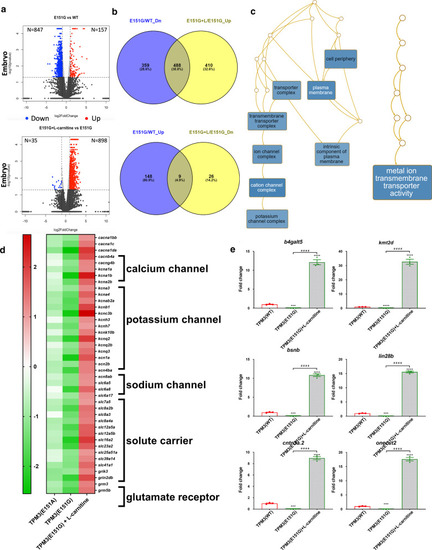
Deep sequencing data for TPM3 transgenic zebrafish. a Volcano plot of genes differentially expressed between TPM3(E151G) mutant compared to TPM3(WT) (upper panel) and TPM3(E151G)-l-carnitine treatment compared to TPM3(E151G) (lower panel). b Venn diagram showing the overlap genes of downregulated in TPM3(E151G) compared to TPM3(WT) and upregulated in TPM3(E151G)-l-carnitine compared to no treatment TPM3(E151G) (upper panel) and overlap genes of upregulated in TPM3(E151G) compared to TPM3(WT) and downregulated in TPM3(E151G)-l-carnitine compared to no treatment TPM3(E151G) (lower panel). c Gene ontology analysis revealed the genes involved in metal ion transmembrane transporter activity are downregulated in TPM3(E151G) and reversed by l-carnitine treatment. d Unsupervised cluster analysis and heat-map including genes involved in calcium, potassium and sodium channel, solute carriers, glutamate receptor are downregulated in TPM3(E151A), reduced more in TPM3(E151G), and upregulated by l-carnitine treatment. The red and green indicate high and low expression of Log2 ratio, respectively. The results were obtained from next-generation deep sequencing. e The expression pattern of selected candidate genes of muscle specimens from embryos of TPM3(E151G) and l-carnitine-treated TPM3(E151G) compared with TPM3(WT) transgenic fish by qRT-PCR. Statistical significance was determined using a t-test, *0.01 < P ≤ 0.05; **0.001 < P ≤ 0.01; ***0.0001 < P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001
|

