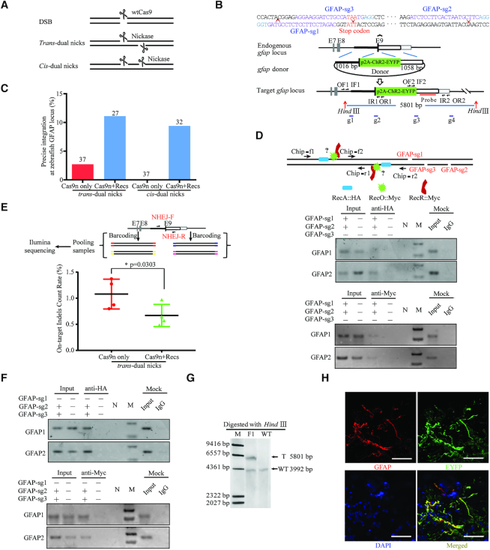
Design and optimisation of dual nicks-based gene KI at the gfap locus in zebrafish. (A) Schematic illustrating DNA break types. (B) Schematic overview of the strategy to generate a GFAP-p2A-ChR2-EYFP KI allele. The nested PCR primers used for knock-in identification are shown (Supplementary Table S4). (C) Germline transmission rate of ChR2-EYFP precise integration at the gfap locus with trans- and cis-dual nicks. (D) ChIP assay at the gfap locus subjected to trans-dual nicks processing. Each sample contained 500 embryos and three replicates were performed. (E) On-target indels analysis using Next-Gen-based multiplexed sequencing. The ratio data was presented as the percentage of reads with indels to the total reads according to the reference (62). Each sample contained 30 embryos and two replicates were performed. Comparisons between groups were analyzed with Student's t-test. * indicates P < 0.05. Error bars denote s.d. (F) ChIP assay at the gfap locus subjected to cis-dual nicks processing. Each sample contained 500 embryos and three replicates were performed. (G) Representative Southern blotting analysis of the GFAP-p2A-ChR2-EYFP targeted allele. T, KI target band. WT, wild type band. (H) ChR2-EYFP signals in the adult brain sections (hindbrain), nuclei in blue were stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 50 μm.
|

