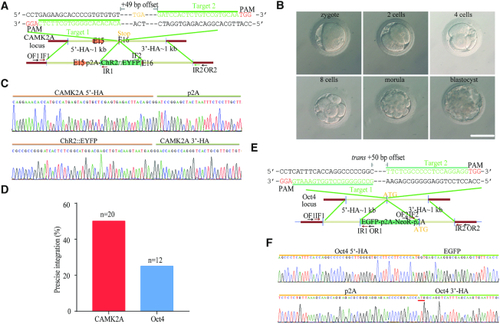
Trans-dual nicks with RecOFAR enable precise and efficient genome knock-in in monkey embryos. (A) Schematic overview of strategy to generate a CAMK2A-p2A- ChR2::EYFP knock-in allele. The nested PCR primers used for knock-in identification are shown (Supplementary Table S4). Two targets are shown with green. The offset distance between two targets is 49 bp. (B) Representative pictures of monkey embryos at distinct stages (Scale bar = 100 μm). The embryos at the morula/blastocyst stage were collected for genome extraction and analysis. (C) Successful HR of CAMK2A-p2A- ChR2::EYFP was confirmed by Sanger sequencing of the PCR amplicon. (D) Efficiencies of p2A-ChR2-EYFP precise integration at the CAMK2A locus and EGFP-p2A-NeoR-p2A precise integration at the Oct4 locus in monkey embryos. (E) Schematic overview of strategy to generate an EGFP-p2A-NeoR-p2A-Oct4 knock-in allele. The nested PCR primers used for knock-in identification are shown (Supplementary Table S4). Two targets are shown with green. The offset distance between two targets is 50 bp. (F) Successful HR of EGFP-p2A-NeoR-p2A-Oct4 was confirmed by Sanger sequencing of the PCR amplicon.
|