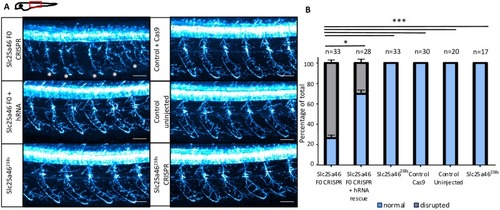
Fig 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-200406-91
- Publication
- Buglo et al., 2020 - Genetic compensation in a stable slc25a46 mutant zebrafish: A case for using F0 CRISPR mutagenesis to study phenotypes caused by inherited disease
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
CRISPR/Cas9 targeting of |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | Long-pec to Days 7-13 |