Fig 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-191230-1070
- Publication
- Marquart et al., 2019 - Prepontine non-giant neurons drive flexible escape behavior in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
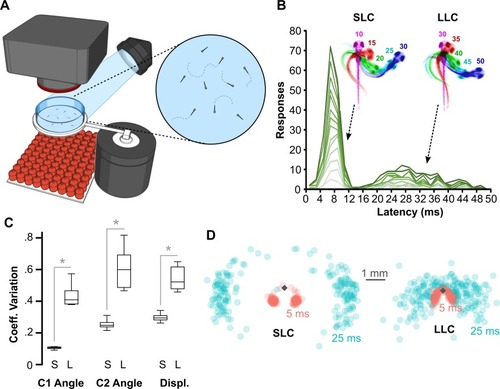
(A) Schematic of behavioral experiments in free-swimming larvae: groups of 15–20 6-dpf larvae were imaged from above at 1,000 frames per second with a high-speed camera. An infrared LED array below provided illumination. Nondirectional acoustic/vibratory stimuli were delivered to the arena by a minishaker. (B) Frequency histogram of response latencies for individual larvae ( |