Fig 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-191230-1074
- Publication
- Marquart et al., 2019 - Prepontine non-giant neurons drive flexible escape behavior in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
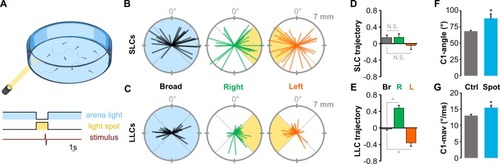
(A) Schematic of experiment measuring escape direction under broad-field illumination or in darkness with only a light spot illuminated. Scale bar 1 s. (B-C) Thirty representative SLC (B) and LLC (C) escape trajectories of larvae to a nondirectional acoustic/vibratory stimulus when under broad-field illumination (“Broad”) or when oriented to the left or to the right of a light spot. Escape direction is plotted radially and net displacement axially. (D-E) Mean direction choice (−1 all left; +1 all right) for SLC (D) and LLC (E) responses under broad-field illumination (“Br”; SLC, |