Fig 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-191230-1073
- Publication
- Marquart et al., 2019 - Prepontine non-giant neurons drive flexible escape behavior in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
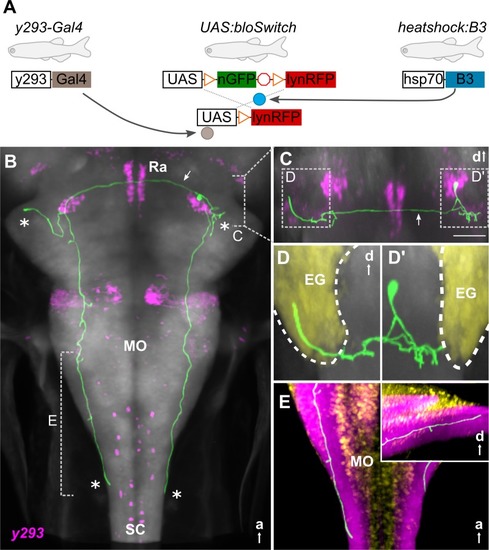
(A) Schematic of 3 transgene system used for B3-recombinase–based neuronal tracing. (B-E) Representative traced neuron in 6-dpf larva (green, for others, see |