Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-190823-7
- Publication
- Colak-Champollion et al., 2019 - Cadherin-Mediated Cell Coupling Coordinates Chemokine Sensing across Collectively Migrating Cells
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
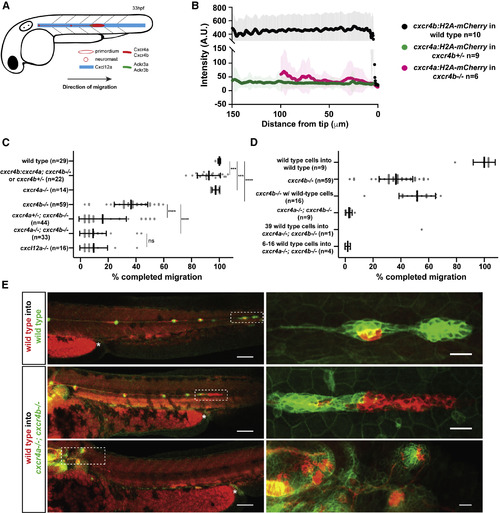
A small Number of Cxcr4-Expressing Cells Cannot Restore Migration of Primordia Lacking Cxcr4 Activity (A) Schematic of primordium migration and chemokine signaling system in primordium. (B) Fluorescent intensity quantification of cxcr4b transcriptional reporter in wild-type primordia (black) and cxcr4a transcriptional reporter in cxcr4bheterozygous (green) and cxcr4b mutant primordia (pink) in 33–36 hpf embryos. Fluorescent intensities were averaged along the front-to-back axis of the primordia. Mean, SD, and n are indicated. (C) Quantification of primordium migration in 48 hpf embryos of indicated genotypes. Note that the cxcr4b:cxcr4a embryos originated from a cross that yielded on average 50% cxcr4b−/− and 50% cxcr4b+/− embryos. Grey dots represent individual data points. Sample size is as indicated. Vertical and horizontal black lines indicate mean and SD, respectively. ∗∗∗ = p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗ = p < 0.0001; ns, not significant (Mann-Whitney test). (D) Quantification of the migration defects in cxcr4 mutants and degree of migration restoration in chimeric primordia. Note that the number of wild-type cells for the chimeras includes wild-type cells in the neuromasts and the primordium. (E) Sum projections of fixed chimeric embryos of indicated genotypes at 48 hpf. Magnifications of primordia in left panels indicated by dashed white rectangles are shown in the panels on the right. The asterisks mark the yolk extension. Scale bars in left and right panels correspond to 100 μm and 20 μm, respectively. See also Figure S1 and Methods S2.
|