Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-190812-29
- Publication
- Chen et al., 2019 - Cerebrovascular Injuries Induce Lymphatic Invasion into Brain Parenchyma to Guide Vascular Regeneration in Zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
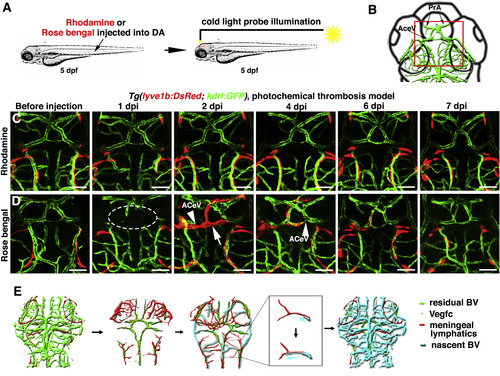
The Temporary Ingrown Lymphatics-Mediated Cerebrovascular Regeneration Is Conserved in the Photochemical Brain Thrombosis Model (A) Technical procedures of the cold-light-induced thrombosis in the zebrafish brain. (B) The red box indicates the image area in (C) and (D). Dorsal view, anterior upward. (C) DA injection of Rhodamine followed by cold light illumination was ineffective on local brain blood vessels (n = 10/10). Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) 1 day post DA injection of Rosa bengal and a 600-s-illumination (1 dpi), local cerebrovascular damage was evident in the illuminated area (dotted circle). By 2 dpi, meningeal lymphatics (arrow) grew into the injured area. Nascent blood vessels (ACeV) grew along the ingrown lymphatics, and vascular regeneration fulfilled by 4 dpi. From 6 to 7 dpi, the ingrown lymphatics become clear from the injured area (n = 15/20). Arrowheads indicate the leading edge of growing blood vessels. Scale bar, 50 μm. See also Figure S7 and Video S6. (E) Illustrations of the ingrown lymphatics-mediated brain vascular regeneration. AceV, anterior (rostral) cerebral vein; BV, blood vessel; PrA, prosencephalic artery. |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 49(5), Chen, J., He, J., Ni, R., Yang, Q., Zhang, Y., Luo, L., Cerebrovascular Injuries Induce Lymphatic Invasion into Brain Parenchyma to Guide Vascular Regeneration in Zebrafish, 697-710.e5, Copyright (2019) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell