Fig. 3
|
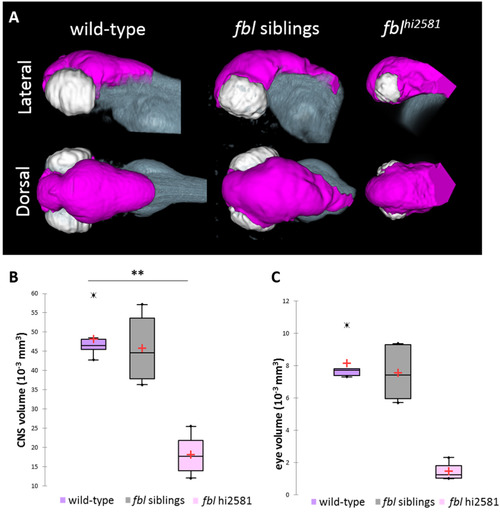
The fblhi2581Tg mutation mostly affects midbrain structures from 24 hpf. (A) Volume rendering of the DiI-positive domains (gray) and surface rendering of a manual segmentation of the CNS (magenta) and eye (white) based on the DiI signal in 3dpf wild-type, fbl siblings and fblhi2581Tg mutant embryos. fbl mutant larvae display an apparent reduction of the CNS volume compared to their siblings or wild-type larvae Lateral views: anterior to the left, dorsal to the top. Dorsal view: anterior to the left, right to the top. (B) Quantification of mean CNS volume highlights a significant difference between fbl mutants, their siblings and wild-type larvae. Statistical analyses were performed on six samples per condition. p-value: .003 (Kruskal-Wallis test). (C) Quantification of mean eye volume highlights a significant difference between fbl mutants, their siblings and wild-type larvae. Statistical analyses were performed on the mean size of both eye of six samples per condition. p-value: .005 (Kruskal-Wallis test). Purple: wild-type, gray: fbl siblings, pink: fblhi2581Tg. Scale bar: 100 µm. Anterior is to the left. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Protruding-mouth |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 437(1), Bouffard, S., Dambroise, E., Brombin, A., Lempereur, S., Hatin, I., Simion, M., Corre, R., Bourrat, F., Joly, J.S., Jamen, F., Fibrillarin is essential for S-phase progression and neuronal differentiation in zebrafish dorsal midbrain and retina, 1-16, Copyright (2018) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.