Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-180404-28
- Publication
- Sakamaki et al., 2015 - Conservation of structure and function in vertebrate c-FLIP proteins despite rapid evolutionary change
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
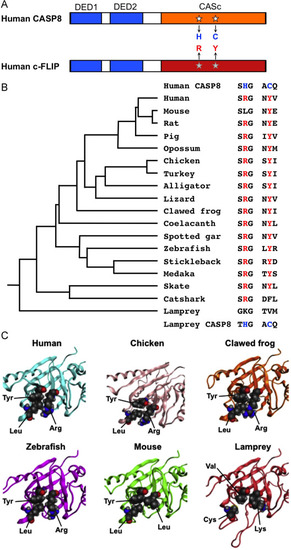
The specified amino acid substitutions of the CASc domain and their evolutionary conservation. (A) A schematic diagram of human CASP8 and c-FLIP proteins. Two DED motifs, a CASc protease domain, and a CASc* protease-like domain are indicated by boxes, respectively. White stars indicate the position of the essential amino acid residues, histidine (H) and cysteine (C) for the catalytic dyad formation in CASP8, whereas the gray stars indicate arginine (R) and tyrosine (Y) of c-FLIP positionally corresponding to two amino acid residues of CASP8, and are also coincident with positions (1) and (2), as shown in Fig. 1A. (B) A summary of critical amino acid residues of c-FLIP proteins conserved in vertebrates. Both the arginine (R) and tyrosine (Y) residues are evolutionarily conserved in most bony vertebrates. In the mouse c-Flip protein, the arginine residue is exceptionally changed to leucine. In the fish lineage, a phenylalanine (F) residue instead of tyrosine is present in the catshark whereas both lysine (K) and valine (V) residues are present at these two critical positions in the lamprey. A taxonomic tree of the species shown at the left was generated based on the previous study [70]. (C) Closeup views of the pseudocatalytic triad of c-FLIP proteins. The arginine, tyrosine, and leucine residues, which are shown in spheres, in human, chicken, clawed frog, and zebrafish c-FLIP proteins are brought close together in the three-dimensional shape forming a triad. In the lamprey, c-FLIP includes lysine, valine, and cysteine residues instead of the conserved amino acids, resulting in the failure of the triad formation. As mouse c-FLIP has replaced the arginine residue with leucine (L), there is little interaction with another leucine. The gray, red, and blue spheres indicate C, O, and N atoms, respectively. |