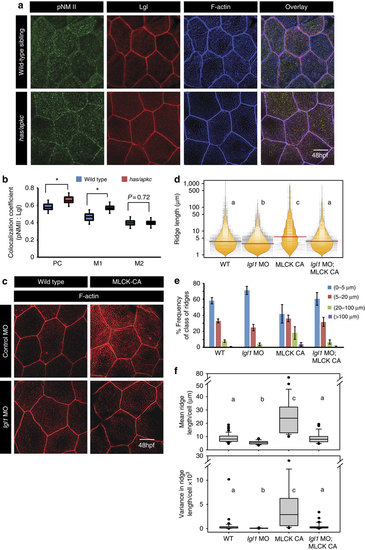
Both Lgl and active MyosinII are required to build long ridges. Immuno-colocalization using anti pNMII, anti-Lgl2 antibodies and phalloidin (a) in wild- type and has/apkc mutant at 48 hpf. Graphical representation (b) of colocalization coefficients for pNMII and Lgl by Pearson’s method and Manders’ overlap of pNMII with Lgl (M1) and Lgl with pNMII (M2) in wild-type and has/apkc mutant embryos at 48 hpf. Phalloidin stainings (c) in embryos injected with control morpholino, MLCK-CA+control morpholino, lgl1 morpholino and MLCK-CA+lgl1 morpholino at 48 hpf, followed by ridge length measurements and visualization of distribution of ridge lengths and medians using bean plots (d). The same data is presented as percentage frequency distribution of ridges in short (0-5 µm), intermediate (5-20 µm), long (20-100 µm) and very long (>100 µm) categories (e). The box-whisker plots (f) represent distributions of means and variances of ridge lengths for individual cells from various genetic conditions. In d and f, the distributions sharing the same alphabet do not differ significantly (Dunn’s multiple comparisons test, P-value<0.05). Error bars in e are for the s.d. Asterisks in b indicate significant difference at P<0.001 by Student’s t-test. Scale bars in a and c is equivalent to 10 µm.
|

