Fig. S5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-160503-29
- Publication
- Jeradi et al., 2016 - Retinoic acid-induced premature osteoblast-to-preosteocyte transitioning has multiple effects on calvarial development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
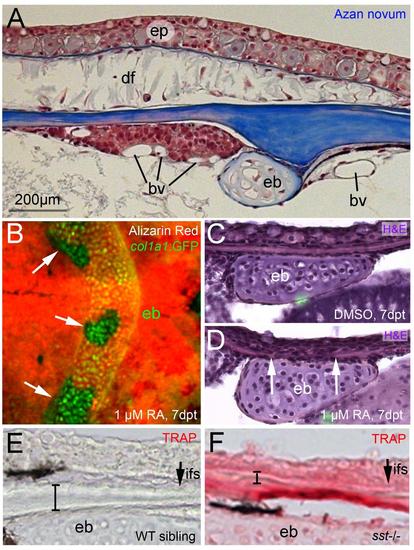
RA-induced calvarial fragmentation occurs primarily at the level of the epiphyseal bar. (A) Azan novum staining of sagittal section through head of 1 year old untreated fish; anterior to the left; region of epiphyseal bar. Directly anterior of the epiphyseal bar is a distinct tissue that is tightly associated with the calvarial plate, suggesting that it is extracephalic. It is highly vascularized, and was not found at any other position along the anterior-posterior length of the brain case. Compare also with Fig. S3D and with Fig. 7I-L, showing that this tissue displays strong cyp26b1 expression upon RA treatment. (B) tg(col1a1:GFP) fish (Kague et al., 2012) after RA-treatment and in vivo alizarin red staining; dorsal view on head region. The holes directly above the GFP-positive epiphyseal bar are indicated with arrows. (C,D) Sagittal sections through epiphyseal bar region of fish after treatment with 1µM DMSO (B) or 1µM RA (C); H&E staining; in (D) the borders of the calvarial hole are indicated with arrows. (E,F) Magnified views of images shown in Figure 3P,Q; transverse sections through epiphyseal bar region of wild-type sibling (D) and sst mutant (E); TRAP staining; the interfrontal suture (ifs) is indicated with an arrow, the thickness of the calvarial plate with a bar. Abbreviations: bv, blood vessel; df, dermal fibroblast; eb, epiphyseal bar; ep, epidermis; fp, frontal plate; ifs, interfrontal suture. |