Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-160503-21
- Publication
- Jeradi et al., 2016 - Retinoic acid-induced premature osteoblast-to-preosteocyte transitioning has multiple effects on calvarial development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
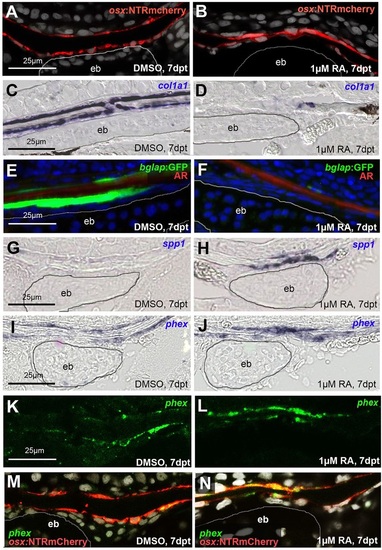
RA induces premature osteoblast-to-preosteocyte transitioning at calvarial fragmentation sites. A,B,G-N show sagittal, and C-F show transverse sections through the fragmentation sites above the epiphyseal bar (eb; outlined) of the frontal plate of SL9-10 wild-type fish treated as indicated. (A,B) The number of osx-expressing cells, as assessed in tg(osx:NTR-mCherry), is unaltered upon RA treatment (9.0±1.26 cells in defined area above epiphyseal bar in DMSO control versus 9.2±1.06 cells in corresponding region of RA-treated fish; n=12 confocal stacks from three independent specimen for each condition). In B, the space separating the two osx-positive lines is strongly reduced, reflecting the thinning or complete loss of the calvarial plate. (C,D) In situ hybridizations, revealing strongly impaired expression of the collagen gene col1a1 in bone-lining cells of the RA-treated fish. (E,F) Expression of bglap, a marker for mature osteoblasts, as assessed in tg(bglap:GFP), is downregulated in RA-treated sample. (G-J) In situ hybridizations, revealing increased expression of spp1 (G,H) and the preosteocyte marker phex (I,J) in bone-lining cells of the RA-treated fish. (K-M) phex in situ hybridization (K,L; green), counterstained via anti-RFP immunolabeling of osteogenic cells expressing the osx:NTRmCherry transgene (red; merged images in M,N). phex induction by RA is most prominent in osteogenic cells above the epiphyseal bar. |