FIGURE
Fig. 6
Fig. 6
|
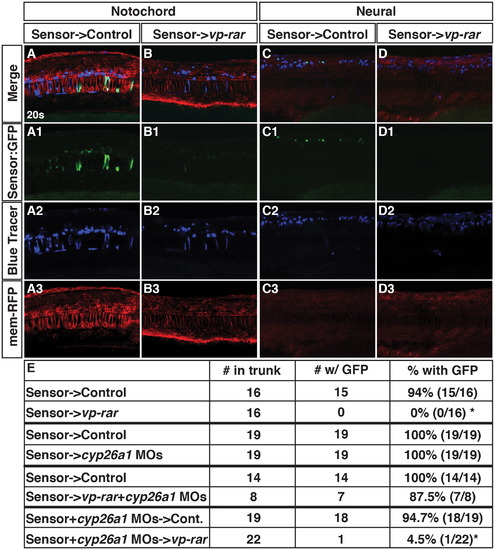
Cyp26a1 has cell non-autonomous consequences on RA signaling levels within the local environment. (A–A3, C–C3) Tg(β-actin:GDBD-RLBD);(UAS:EGFP) donor cells transplanted into WT hosts injected with mrfp mRNA have EGFP expression in the notochord and spinal cord. (B–B3, D–D3) Tg(β-actin:GDBD-RLBD);(UAS:EGFP) donor cells transplanted vp-rar mRNA injected hosts with mrfp mRNA have severely dampened GFP expression. (E) Table showing summary of blastula transplantation results. Asterisks indicate statistically different from controls (p<0.05) using a modified chi-square test. |
Expression Data
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 405(1), Rydeen, A., Voisin, N., D'Aniello, E., Ravisankar, P., Devignes, C.S., Waxman, J.S., Excessive feedback of Cyp26a1 promotes cell non-autonomous loss of retinoic acid signaling, 47-55, Copyright (2015) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.