Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-150717-6
- Publication
- Stoyek et al., 2015 - Intrinsic and extrinsic innervation of the heart in zebrafish (Danio rerio)
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
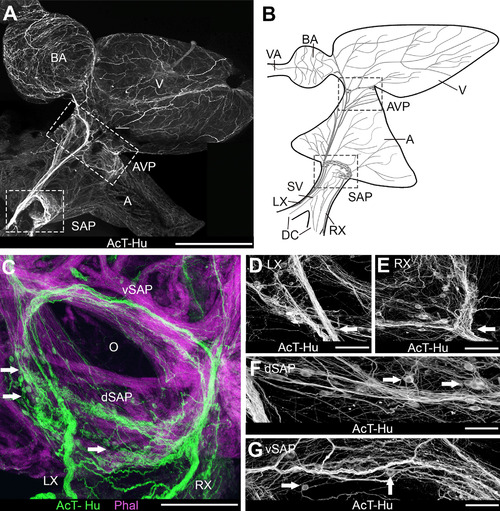
Organization of intracardiac nervous system demonstrated with acetylated tubulin (AcT) and human neuronal protein (Hu) immunohistochemistry. A,B: Whole mount of heart (A) and schematic (B) show an overview of the chambers of the heart and the major elements of cardiac innervation. Schematic represents the heart as it would appear after removal from the body for making whole-mount cardiac preparations. Blood passes serially from the paired ducts of Cuvier (DC) into the sinus venosus (SV), through the sinoatrial valves and into the atrium (A), then into the ventricle (V), the bulbus arteriosus (BA), and the ventral aorta (VA) to the gills. The lower boxed areas in A and B are the region containing the sinoatrial valve, where the sinoatrial plexus (SAP) was located. In A the upper box indicates the region of the atrioventricular plexus (AVP) at the atrioventricular junction. RX, LX, right and left vagosympathetic trunks. C-G: Details of innervation in the region of the sinoatrial valve (O: valve ostium). C: Cardiac myocytes were labeled with phalloidin (Phal); arrows indicate neuronal somata. dSAP, vSAP: dorsal and ventral regions, respectively, of SAP. D,E: Details of SAP where LX and RX, respectively (arrows), enter the plexus. Somata were clustered into ganglia in each region. F,G: Dorsal and ventral SAP, between the areas shown in D,E. Arrows indicate somata. Scale bars = 1 mm in A; 250 µm for B; 100 µm in C,D; 75 µm in E-G. |