Fig. S2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-130411-6
- Publication
- Boglev et al., 2013 - Autophagy induction is a tor- and tp53-independent cell survival response in a zebrafish model of disrupted ribosome biogenesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
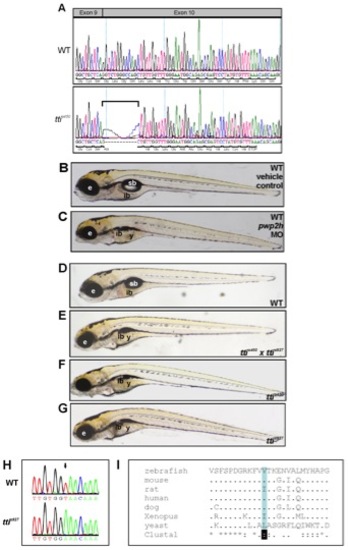
pwp2h is the mutated gene in ttis450. (A) Sequence of pwp2h in WT and ttis450 cDNA reveals that ttis450 larvae utilize a cryptic splice site in exon 10 due to a mutation in the splice acceptor site in intron 9. This results in an 11 bp deletion (bracket) which causes a frame-shift in the pwp2h coding sequence resulting in 13 aberrant amino acids and a premature stop codon in exon 10. (B, C) Upon microinjection into the yolk of 1–4 cell WT zebrafish embryos, a pwp2h-targeted MO (15 ng) produces a robust ttis450 phenotype at 120 hpf (C). Vehicle-injected controls appear WT (B). (D–G) Non-complementation of 2 independent pwph2 alleles confirms that pwph2 is the mutated gene in ttis450. Heterozygous ttis450 carriers were crossed with heterozygous carriers of s927, an independent pwph2 allele identified in the 2-CLIP screen [30]. One quarter of the offspring are compound ttis450;ttis927 mutants (E) and exhibit the ttis450 phenotype (F) at 120 hpf including impaired development of the digestive organs, eye and craniofacial structures. Other panels show WT (D) and ttis927 mutant (G) larvae at 120 hpf. These data indicate that both alleles correspond to the same genetic locus. e, eye; ib, intestinal bulb; sb, swim bladder; y, yolk. (H) The nucleotide sequence of pwp2h cDNA generated from ttis927 larvae contains a T→A transversion (arrow). (I) The base change in ttis927 results in a highly conserved branched amino acid (valine, shaded blue) being replaced by glutamic acid. Alignment was performed using ClustalW. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Day 5 |