Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-130326-25
- Publication
- Mugoni et al., 2013 - Ubiad1 Is an Antioxidant Enzyme that Regulates eNOS Activity by CoQ10 Synthesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
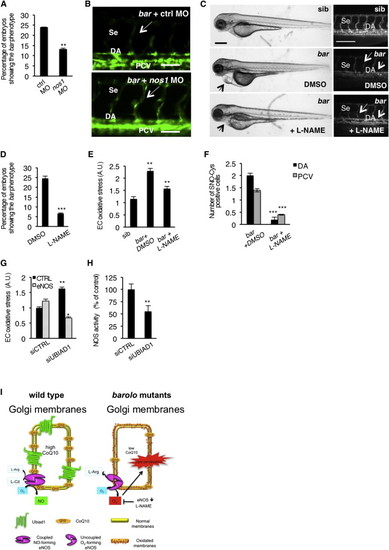
NOS Activity in Cardiovascular Tissues Is Regulated by UBIAD1 and CoQ10(A) Knockdown of endothelial nitric oxide synthase 1 by morpholino (nos1 MO) reduces the penetrance of bar phenotype at 72 hpf.(B) Knockdown of nos1 rescue endothelial integrity defects of bar mutants. Images of Se of bar at 72 hpf injected with nos1 morpholino (bar + nos1MO) or control morpholino (bar + ctrl MO) Scale bar, 50 µm.(C) Bright-field images (left) and fluorescent micrographs showing the trunk vasculature (right) of Tg(kdrl:GFP)s843bar treated from 48 hpf with the specific eNOS inhibitor L-NAME (500 µM). Heart failure (arrowhead) and endothelial regression (arrows) were fully rescued by L-NAME treatment. Scale bar, 100 µm.(D) Penetrance of the bar phenotype at 65 hpf is significantly decreased by inhibition of eNOS activity with L-NAME treatment from 32 hpf.(E) Oxidative stress level in ECs derived from Tg(kdrl:GFP)s843bar mutant embryos is decreased by L-NAME treatment.(F) eNOS inhibition by L-NAME treatment significantly reduces ECs positive for S-nitroso-cysteine (SNO-Cys) in DA and PCV of bar embryos.(G) Silencing of eNOS (sieNOS) rescues oxidative stress induced by the lack of UBIAD1 (siUBIAD1). Silencing eNOS alone did not decrease ROS level in ECs.(H) Silencing of UBIAD1 gene (siUBIAD1) causes a significant decrease of eNOS activity in ECs evaluated as [3H]-L-citrulline.(I) Schematic representation of Ubiad1 molecular function in CoQ10 production and maintenance of nitrix oxide (NO) signaling. In wild-type cells, Ubiad1 localizes in the Golgi compartment and produces CoenzymeQ10 (CoQ10), an antioxidant molecule, important to counteract oxidative damage in particular in cellular membranes (cytosol and plasma membrane). In the Golgi compartment CoQ10 as an electron carrier might also play a fundamental role as a cofactor for eNOS activity by maintaining its “coupled” conformation and allowing normal NO production. On the other hand, lack of UBIAD1 and lowering of CoQ10, as occurs in the cardiovascular tissues of bar mutants, might “uncouple” eNOS causing loss of NO production and consequently reactive oxygen species overload leading to cellular oxidative damage (e.g., lipid peroxidation). Thereby, the “barolo” phenotypes can be rescued by impairment of eNOS activity or expression. Data are means ± SEM. p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.001. See also Figure S6. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Protruding-mouth |
Reprinted from Cell, 152(3), Mugoni, V., Postel, R., Catanzaro, V., De Luca, E., Turco, E., Digilio, G., Silengo, L., Murphy, M.P., Medana, C., Stainier, D.Y., Bakkers, J., and Santoro, M.M., Ubiad1 Is an Antioxidant Enzyme that Regulates eNOS Activity by CoQ10 Synthesis, 504-518, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Cell