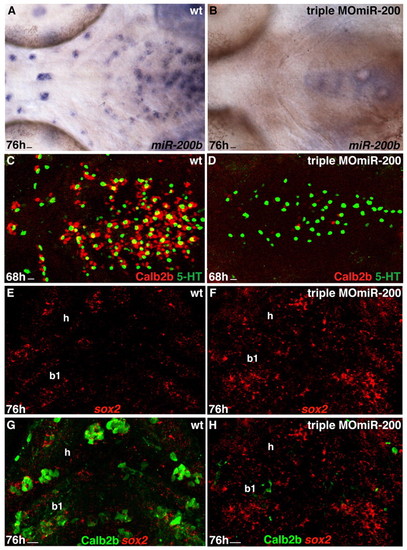
miR-200 knockdown results in reduction of taste bud cells. Experimental conditions are indicated in the top right-hand corner, embryonic stage and scale bar are in the bottom left-hand corner and marker expression is in the bottom right-hand corner. Anterior is towards the left. Scale bars: 8 μm. (A,B) Whole-mount ventral views of wild-type and triple MOmiR-200-injected embryo labeled with miR-200b probe. miR-200b expression is absent from the pharyngeal epithelium of the morpholino-injected embryo. (C,D) Whole-mount ventral views of taste buds of wild-type and triple MOmiR-200-injected embryo labeled with anti-Calb2b (red) and anti-5HT (green). Note the strong and mild reduction in the numbers of Calb2b+ and 5HT+ cells, respectively in the triple MOmiR-200 injected embryo (D) compared with the wild-type control. (E-H) Ventral view, anterior towards the top. Confocal projection of hyoid (h) and first branchial arch (b1) epithelium of a wild-type and a triple MOmiR-200 injected embryo labeled with the sox2 probe (E-H) and anti-Calb2b (G,H). Calb2b expression is severely decreased but sox2 expression is increased in the triple MOmiR-200 injected embryo (F,H) compared with the control (E,G).
|

