Fig. S8
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-101122-74
- Publication
- North et al., 2010 - PGE2-regulated wnt signaling and N-acetylcysteine are synergistically hepatoprotective in zebrafish acetaminophen injury
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
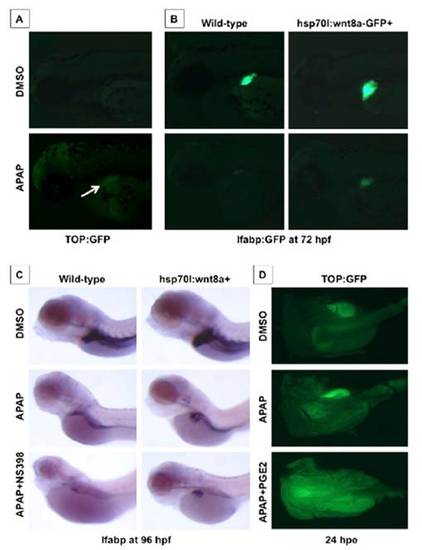
Prostaglandin production influences the effects of wnt8a activation on APAP liver toxicity. (A) Effect of APAP from 48–72 hpf on wnt activity in TOP:dGFP wnt reporter line; APAP caused wnt activation specifically in the embryonic liver. (B) Transgenic Tg(hsp70l:wnt8a-GFP)w34; lfabp:GFP embryos heat-shocked at 48 hpf were exposed to APAP; wnt8a induction rescued liver-specific GFP expression after APAP. (C) Transgenic Tg(hsp70l:wnt8a-GFP)w34 embryos were heat-shocked at 38 °C for 20 min at 48 hpf and exposed to 10 mM APAP; in situ hybridization for lfabp was performed at 96 hpf. wnt8a induction enlarged the liver in untreated embryos and rescued the liver after APAP exposure. Inhibition of PGE2 production by the cox2 inhibitor NS398 (10 μM) enhanced APAP toxicity and diminished the positive effects of wnt8 activation. (D) Adult TOP:GFP wnt reporter fish were exposed to APAP (10 mM) alone or concomitantly to dmPGE2 (10 μM). After 24 h, fish were sacrificed, and the livers were dissected and imaged using a fluorescent dissecting microscope. There is no detectable baseline wnt activity in the untreated liver. APAP exposure enhances wnt activity, which is further increased after additional dmPGE2 exposure. |