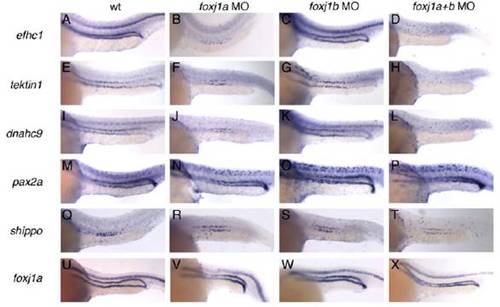
Fig. S6
|
efhc1, tektin-1, and dnahc9 expression in the pronephros is foxj1a and foxj1b dependent. In situ hybridization analysis in control, foxj1a morphant (MO), foxj1b MO, and foxj1a+b double morphants at 24 hpf demonstrated that combined foxj1a/b double knockdown uniformly abolished expression of cilia motility associated genes but not other kidney specific markers or foxj1a itself. (A-D) EF-hand containing domain 1 (efhc1), (E-H) tektin-1, (I-K) dynein heavy chain 9 (dnahc9), (M-P) pax2a, (Q-T) shippo, (U-X) foxj1a (n > 15 embryos for each condition). (A, E, I, M, Q, U) Control embryos; (B, F, J, N, R, V) foxj1a MO; (C, G, K, O, S, W) foxj1b MO; (D, H, L, P, T, X) combined foxj1a/b knockdown. |