Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-101104-5
- Publication
- Raphael et al., 2010 - Schwann cells reposition a peripheral nerve to isolate it from postembryonic remodeling of its targets
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
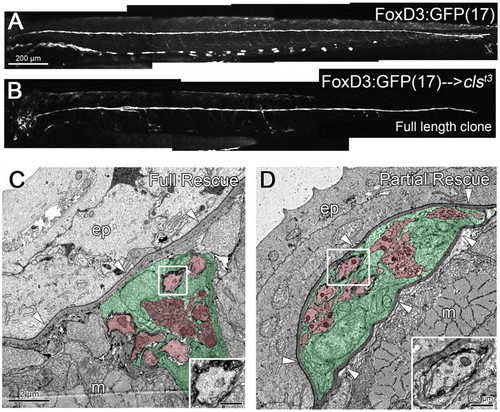
Full-length clones of transplanted wild-type Schwann cells can rescue nerve position in sox10/clst3 mutants. (A) Wild-type 3 dpf embryo carrying the FoxD3:GFP(17) transgene, labeling the PLLn, motor nerves and some pigment cells. (B) FoxD3:GFP(17) cells have been transplanted into a sox10/clst3 mutant host, creating a clone of wild-type Schwann cells that traverse the entire length of the PLLn (3 dpf). (C) Transplanted wild-type Schwann cells can reposition the mutant nerve in the subepidermal space, below the basement membrane (arrowheads). (D) Transplanted wild-type Schwann cells partially rescue the mutant nerve, positioning it within the epidermal basement membrane (arrowheads). Insets show the presence of myelinated axons in C,D. Scale bars: 200 μm for A,B; 2 μm for C,D. Schwann cells are pseudocolored green and axons red in C,D. Abbreviations: ep, epidermis; m, muscle. |